
This article is a step-by-step tutorial on how to configure DNS forwarding in Windows Server 2012 R2 version. In the continuation of this tutorial, we will teach you how to create a DNS forwarder using DNS Manager and PowerShell.
Simply put, DNS forwarding is asking for help finding an address. The default method is that DNS server sends queries that cannot be answered to a list of DNS servers on the Internet called root hints.
But if DNS forwarding is configured, it sends queries to the destination we call the forwarder.
Table of Contents
How to configure DNS Forwarding in Windows Server 2012 R2 version
DNS server installation on Windows Server is done with the help of DNS manager or PowerShell.
How to create a DNS forwarder using DNS Manager
In the server where the DNS server roll is installed, open Sever Manager and then go to Tool> DNS to enter DNS Manager.

Right-click on the DNS Server name and click Properties.

Enter the Forwarder tab and click Edit.
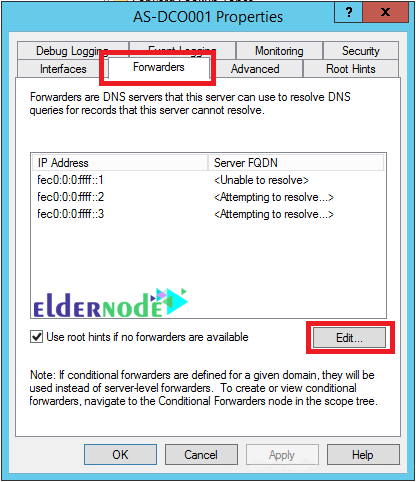
Enter the IP address of the other DNS server (forwarder) and then press Enter. If the IP address is valid, a green tick will be displayed. Do this for each other forwarder server.
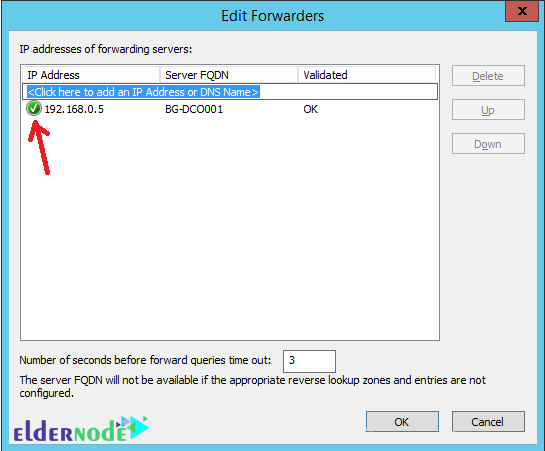
Click OK to save the settings.
How to create a DNS forwarder using PowerShell
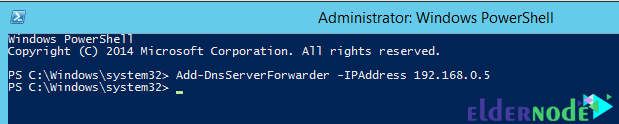
As we said, you can do this with PowerShell as well. To do this, enter the following command:
Add-DnsServerForwarder –IPAddress < IP Address >The following command is used for the same purpose:
Set-DnsServerForwarder –IPAddress < IP Address >Just enter the relevant IP address to execute the command correctly. You can add multiple forwarders in one command by separating their IP addresses using commas (,). Note that there is a difference between the above two commands. The Add command adds the specified forwarder to the list of forwarders, but the Set command replaces the existing forwarders with the specified IP address.
You can see an example of putting the IP address in the forwarder command in the image below.
How to work with DNS Forwarding on Windows DNS server
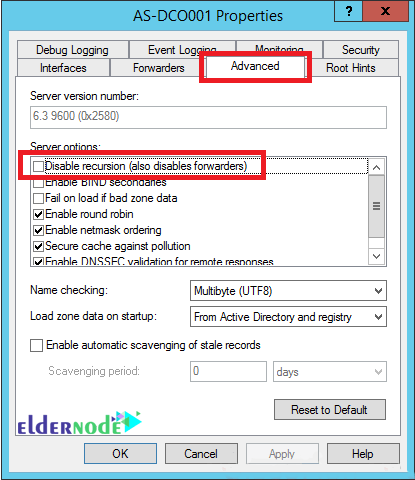
Before configuring DNS forwarding, you need to make sure that recursion is not disabled. DNS forwarding requires recursion to request information from forwarders for clients.
By default, recursion is enabled, but in some cases, it may be disabled. To check this, you need to enter the DNS server settings and go to the Advanced tab. Then in the Server Option section, make sure that the disable recursion option is not checked.
Conclusion
This article teaches you how to configure DNS Forwarding in Windows Server 2012 R2 version using DNS manager and PowerShell. Then the steps for creating a DNS forwarder were explained with pictures. If you are interested in MikroTik, you can refer to the DNS configuration tutorial in MikroTik.





What to do to create other zones in a DNS server?
To create other zones in a DNS server with the current nameservers (for example ns1.yourdomain.com and ns2.yourdomain.com) just use the nameservers and corresponding IPs in the name servers section associated with each zone. Finally, set the relevant nameservers on them through the domain control panel.
What is DNS Forwarder and what does it do?
DNS Forwarder is a DNS server which, as its name implies, is for forwarding DNS queries to DNS servers outside the network.
Why does DNS Server forward Resolve requests?
This is because if the DNS Server configured as DNS Forwarder fails to respond to queries, it will send them to the DNS Servers on its Forwarders list.
What is DNS Root Hints?
Windows-based DNS servers, when installed on a server, have a list of Public IP addresses by default that send Name Resolution requests to Internet addresses to those IP addresses that are in the Public IP addresses that DNS servers are actually Internet so-called DNS Root Hints.
If we set up more than one DNS server in the network, what will be the forwarder settings in it?
If you have more than one DNS Server on the network, you can set two or more as DNS Forwarder. In terms of network performance, setting up one DNS server as a forwarder is more efficient than setting up multiple DNS servers as a forwarder because of the query-based DNS service mechanism.
What are the benefits of setting up a DNS as a Forwarder?
It saves your network bandwidth and greatly increases the response time to queries.