
RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks. This phrase may seem very unfamiliar at first glance, but this technology is easier understand than you might think. RAID was first introduced in 1987 by David Patterson, Randy Katz and Garth Gibson. These people envisioned 6 RAID modes with different features (named from 0 to 5), but today the number of RAID modes has increased. IBM filed a patent in 1977, which was later renamed RAID 4. In 1983, Digital Equipment introduced drives with RAID 1 capability. In 1986, IBM filed another patent, now known as RAID 5. The main purpose of RAID is to store the same data on different disks to prevent data loss when damage and crashes occur on the disks. In this article, we try to acquaint you with Raid and its advantages and disadvantages. Note that to have Raid, you must have a dedicated server and Raid controller to be able to use Raid. You can visit the packages available in Eldernode to purchase a dedicated server.
Table of Contents
Raid Disk (Advantages and Disadvantages)

RAID works by inserting data into multiple disks. By allowing data to enter and exit all of these disks, performance and speed increase. Using multiple disks increases error rate and reduces data loss.
RAID arrays in the operating system are consider as a logical disk and you do not view each disk independently. The size range of data sharing units in RAID starts from 512 bytes and reaches several megabytes. In the continuation of this article, join us by introducing Raid types along with its advantages and disadvantages.
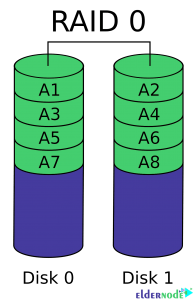
Introduction to Raid Disk 0
In this case, the stored information is split between your disks or so-called “stripes”. For example, if you have two disks, half of the data is storing on one disk and the other half on the other disk. Suppose the system wants to store “100111” data in this state; The first one, the second zero and the third one are stored on disk 1 and the rest on disk 2, and finally will be stored on disk 1 “101” and disk 2 “011”.
Advantages of Raid 0
1. Increase reading and writing speed
2. Usability of the entire volume of disks
3. Low number of disks required
4. Easy to run
Disadvantages of Raid 0
1. If any of the disks are damaged and their data is lost, virtually all of the data is lost.
2. Damage to one disk increases the risk of creating a Bad Sector and damage to another disk.
Ideal use of Raid 0
RAID 0 is not at all suitable for sensitive applications, instead it will be useful in tasks such as editing images and videos due to its high speed. It is also ideal for storing non-critical data that needs to be read or written at high speed. If a user wants to use twee drives to combine the storage capacity of a single volume, he must install one drive in the folder path of another drive. It should be noted that this feature is supported on Linux, OS X and Windows.
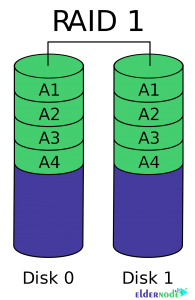
Introduction to Raid 1
In this case, the information is written to your disks in the same way, and your disks contain exactly the same information. For example, “1001” data in this case will be store as “1001” on all disks.
Advantages of Raid 1
1. More information protection
2. If the data on a disk is lost, there is no problem reading the data.
3. Ability to add a new disk to RAID and create the same disk automatically
4. Ability to remove disks from the set of disks and use them independently
5. RAID 1 is a very simple technology.
Disadvantages of Raid 1
1. Slower speed than RAID 0
2. The usable volume is equal to half the total volume.
3. Damage to one disk increases the risk of creating a Bad Sector and damage to another disk.
Ideal use of Raid 1
RAID 1 can be used in accounting systems and small servers. In addition, it is suitable for small servers that use only two data drives.
Introduction to Raid 5
This mode of RAID tries to provide you with the best RAID 0 and RAID 1 modes. One of the features of Raid 5 is to increase the speed without increasing the risk of losing information. You must have at least three disks to use this mode. Two disks are written like RAID 0 and the data is split between the two. Parity bits are then written to the third disk.
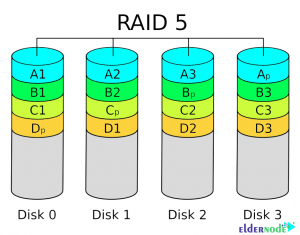
Balance bit is a bit to indicate the number of pairs or individuals and with the help of this data, in case of loss of any of the disks, the system can create a new disk with the data of the other two disks and the information remains undamaged.
Advantages of Raid 5
1. Does not have RAID 0 and RAID 1 problems.
2. High read speed
3. Increase data protection
Disadvantages of Raid 5
1. Minimum number of disks required more than RAID 0 and RAID 1
2. Drive failure affects throughput.
Ideal use of Raid 5
RAID 5 is suitable for servers with a limited number of disks due to its good speed and stability. It is also a comprehensive system that combines efficient storage with good security and good performance. In addition, it is ideal for file and application servers that have a limited number of data drives.
Introduction to Raid 6
This RAID is also called RAID with Double Parity RAID bits, which is actually derived from its structure. How to store data is the same as RAID 5, except that this RAID uses two bits of plugins. That is, it calculates parity twice in two different ways and distributes it on two different hard disks.
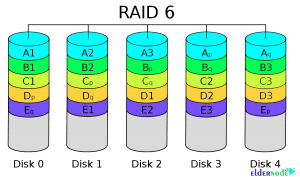
This allows the system to continue working without interruption if both hard disks are destroyed. In fact, the error tolerance of this RAID is 2, which means that if the two drives fail completely, there is still the ability to recover data. If 3 hard drives have a problem, the data will be out of reach. RAID 6 can also be used on SSDs.
Advantages of Raid 6
1. Highest level of fault tolerance and Fault Tolerance
2. RAID6 is actually an advanced version of RAID5 that improves error correction and control. This RAID version provides high reliability and capability in data storage.
3. The best choice for critical and sensitive applications
Disadvantages of Raid 6
1. Highly advanced and complex control circuit design
2. Very slow writing cycle (double parity calculation)
3. Requires N + 2 hard disk drive, due to its two-dimensional parity mode. (N number of normal hard drives)
4. High reliability integration with high functionality
Ideal use of Raid 6
Due to the fact that the number of offline backup hard drives in the RAID 6 model has increased to two, this has increased the security factor in this RAID model compared to the RAID 5 model.
Introduction to Raid Disk 10
This mode is actually RAID 1+0. In this case, the data is first split between a pair of disks such as RAID 0, and then this pair of disks, such as RAID 1, is written to another pair of disks. Of course, this may be done in reverse order, which does not result in change. In this case, at least four disks are need. RAID 10 is more efficient than RAID 1, but it also costs more. In RAID 10, data is first mirrored and then stirped.
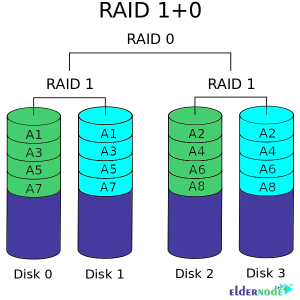
Advantages of Raid 10
1. Does not have RAID 0 and RAID 1 problems.
2. Increase data protection
3. Recovers data much faster than RAID 5
4. Read and write faster than RAID 5
Disadvantages of Raid 10
1. Minimum number of disks required more than RAID 0, RAID 1 and RAID 5
2. The number of unusable disks is higher than RAID 5 and the significant difference in usable volume is high
Ideal use of Raid 10
This Raid is a nested RAID configuration that provides redundancy of RAID 1 along with RAID 0 R/W speed.
Introduce Raid Controller
A RAID controller acts as an interface between the operating system and the physical disks, and presents the disk group as logical units to the operating system. Using a RAID controller improves performance and protects data when it crashes. The RAID controller can be both hardware and software. In the hardware controller, a physical controller manages the array. This physical controller can be in the form of a PCI Express card and is design to support SATA and SCSI formats. The physical controller may also be part of the motherboard.
Software controllers use system hardware resources to perform their function, but do not increase performance as much as hardware controllers.
If the software controllers are not compatible with the system and the hardware controllers are too expensive, the use of an operating system-based RAID or driver is recommending. In this type of controller, the controller chip is installing on the motherboard and all operations are performing by the CPU. So far, this controller works like a software controller; But the difference is that this controller monitors the operation of the RAID after booting up the system. This controller is not as expensive as hardware controllers and has higher performance than software controllers.
Keep in mind that you can have Raid Software with 2 or more hard drives when installing on a dedicated server. If you need to have a Hardware Raid and use it, you must have a dedicated server with a Raid Controller and more than 2 hard drives. In the continuation of this article, we will explain each of these two methods.
Hardware Raid
In this method, the RAID program is run through a processor and RAM embedded in a device independent of the host computer. The hardware can be used seamlessly on the motherboard or a slot card that can be installed on the motherboard.
The easiest way to determine which type of hardware or software RAID is best for your job is to review the specifications or manuals of each. If the proposed method involves a microprocessor (usually an I/O, processor, or in some cases ROC – meaning RAID embedded in the chipset), the proposed method is hardware, and if there is no processor, it is software. It is important to know which method has what effects on your work process and which one is best for you. The effects discussed are as follows:
– Processor performance status when running other programs
– Performance of disks that can be add to the system
– Ease of restoring information after failure
– Advanced data management and monitoring capabilities
– Ability to manage disks simultaneously on different operating systems
– Ability to install a backup battery to upgrade the system cache
Implementing hardware RAID is possible in two ways:
1) as a standalone card
2) Integrated on a special chipset.
Software Raid Disk
An easy way to describe software RAID is to know that it uses your system processor to do its job. This means that the processing needs and power that RAID is supposing to use for its operations are impose on the system processor in addition to the usual processing required by the operating system and the software running on it.
Software RAID is using in two ways:
1) As a pure software solution
In this case, the software will work without any hardware assistance, just using the system features as an application software along with other software running on the operating system. The hard disk used in this method is the same disk on which the operating system is located. Some of these software RAIDs have the ability to integrate with the server operating system along with free programs, which makes this method cheaper.
2) As a hybrid solution that includes hardware designed to improve processor performance
In this method, RAID software works with the help of hardware added to the motherboard, such as an HBA with a RAID BIOS that fixes the weakness of the previous solution when booting the system. In addition, the hardware drivers used in this method are supporting by most operating systems.
Conclusion
Nowadays, RAID technology is using to increase efficiency, capacity and security. Capacity increase is usually considering in any RAID system. For example, two hard drives can be connect to form a high-capacity storage unit. Increasing efficiency is another reason to use this technology. In a similar example, two hard disks are connect to form a single memory. In this case, the controller can split the data into two parts and put each part on a hard disk. This doubles the efficiency of the storage system for reading and writing information. The third provides security for users’ information. The data is written to two or more hard disks, and if one of the disks has a problem, the information will still be available on the other hard disk. In this article, we tried to acquaint you with the types of Raid along with the advantages and disadvantages of each.




