
In this article, we will teach you how to FTP configuration to prevent Brute-force attacks on Windows Server 2012. We will also limit access to FTP in IIS 8.0. One of the vulnerabilities of the server is brute-force attacks on the password in the FTP service. Since the accounts used for FTP are sometimes the user’s physical accounts on the host operating system, it is theoretically possible to guess the administrator username when the FTP server type is specified.
Once the account name is found, the hacker can launch brute-force attacks. (For example, “administrator” for Windows and root for UNIX operating systems).
Table of Contents
FTP configuration to prevent Brute-force attacks on Windows Server 2012
In IIS 7.5, the FTP introduced by the extensibility API service, which allows developers to use a custom authentication provider, which allows non-Windows accounts to access FTP. This greatly increases the likelihood of attacks for the FTP service, as these FTP accounts are not valid Windows accounts. Therefore, it does not have access to resources outside of the FTP service.
Using the FTP authentication extensibility feature in IIS 7.5, Microsoft offers a way to reduce brute-force attacks for non-Windows accounts by creating a custom authentication provider.
In IIS 8.0 Windows Server 2012, Microsoft has added a security feature that allows all logins to be created without the need for a custom authentication provider. In this tutorial, we will look at the steps needed to limit the frequency of login to prevent brute-force from occurring.
The FTP service can be configured to block access to the FTP service based on the number of failed authentication times over a period of time. When we reach the number of failed logs, the server closes the FTP connection and the FTP client address is blocked for a certain period of time.
Prerequisites to FTP configuration
- Windows Server 2012 with IIS 8.0 and FTP service installed.
Solution to possible bugs in FTP service
There are no bugs for this feature.
How to configure FTP to prevent Brute-force attacks
Repeat the following steps to configure the FTP service to prevent malicious users from accessing the FTP service:
1. Log in as an administrator in Windows Server 2012.
2. Open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
3. In the Connections section, click the server name and then double-click FTP Logon Attempt Restrictions.
4. Check Enable FTP Logon Attempt Restrictions. Then specify the number of times the FTP login failed and the length of time access to the FTP client is blocked.
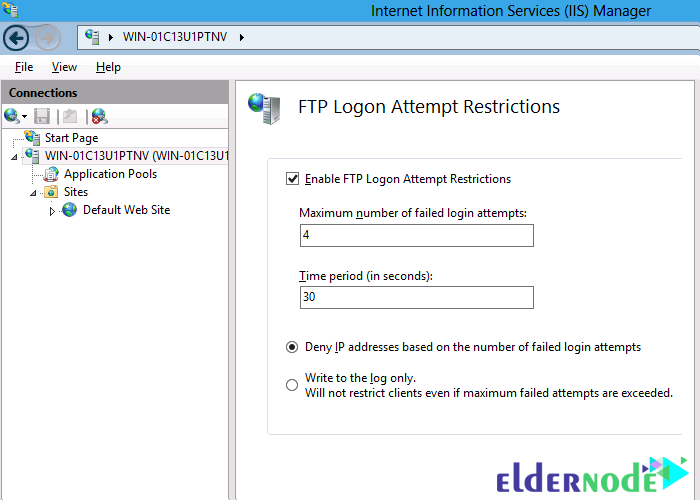
5. Click Apply.
The “Write to the log only” option does not block attempts to log in. It only logs the conditions it had. IT administrators can then test different configuration parameters to assess how these settings affect their users.
Note that FTP Logon Attempt Restrictions are server-level settings. You cannot create these restrictions on any site. Because attackers gain access to your server, not a site, the FTP service blocks malicious users from accessing the server.
Conclusion
This article discusses the FTP configuration to prevent Brute-force attacks on Windows Server 2012. The steps needed to limit the number of times you log in to prevent brute-force were also taught. If you wish, you can read How to Install and Configure the FTP server with PowerShell.





What is the use of FTP?
With ftp you can access your files without the need for RDP.
What is Hybrid brute force attacks and how does it work?
This is one of the most common forms of brute force and uses a list of words in a dictionary for a password. There are other types of attacks that use a list of common passwords. For example, if your password is “password”, a robot can guess your password in a matter of seconds.
What is the purpose of brute force attacks?
– Stealing or disclosing personal information of users in online accounts
– Spread malware or spam or redirect the domain to malicious content
– Create fake content
– Stealing system resources for use in other activities
– Deface the site and access the site administrator documents
Please explain how to view brute force attacks.
No server will tell you that there are such attacks on your service or that someone from an area is testing your site or panel. If you are a network administrator or server administrator, it is important for the security of the website and users to look for its signs, examples of which will be mentioned as examples.
– Failed attacks by an IP address. However, this can be the result of a large organization using a proxy server.
-Sign in with multiple usernames from one IP address. Again, this can simply be from a large organization.
– An unusual pattern of unsuccessful login (a consecutive numerical pattern, etc.)
– Abnormal bandwidth consumption after successful login, which could indicate an attack designed to steal resources.
Is using CAPTCHA effective in preventing brute-force attacks?
Bypassing a Captcha alone may not be difficult for a hacker, but it can create obstacles for potential attackers.
Thank you. That was very helpful!