Bacula is one of the most popular and widely used solutions for backing up and restoring Linux. You can run Bacula entirely on a computer and backup your data to other media such as disks and backup tapes. This is very efficient and relatively easy to use. Bacula is modular due to its modular design and works on a single computer as well as a wide area network with hundreds of devices. In this article, we want to introduce you step by step to How to Install and Configure Bacula on CentOS 8, 7. It should note that you can visit the packages available in Eldernode if you wish to purchase a CentOS VPS server.
Table of Contents
Tutorial Install and Configure Bacula on CentOS 8
Bacula is an open-source application that enables you to do the following:
1- Backup data.
2- Check the data in the networks.
3- Recover damaged or lost files quickly.
In the next section, we will teach you how to Install Bacula on CentOS 8. Then in the last section, we show how to configure Bacula. Please stay tuned for the rest of this article.
Install Bacula on CentOS 8 | CentOS 7
In this section, we will discuss how to install Bacula on CentOS 8. Note that Bacula can work with the PostgreSQL database management system. So it is enough to do the following steps in order:
dnf install postgresql-serverpostgresql-setup initdbsystemctl enable --now postgresqlThe next step is to create a user for Bacula. To do this, run the following commands in order:
sudo su - postgres$ createuser bacula$ psqlpsql (10.14)Type "help" for help.postgres=# ALTER USER bacula PASSWORD 'bacula';ALTER ROLEpostgres=# ALTER USER bacula LOGIN SUPERUSER CREATEDB CREATEROLE;ALTER ROLEpostgres=# \q$ exitlogoutNow you should uncomment the following setting in the /var/lib/pgsql/data/postgresql.conf file:
listen_addresses = 'localhost'Now you need to change the connection configuration to the following format in the /var/lib/pgsql/data/pg_hba.conf file:
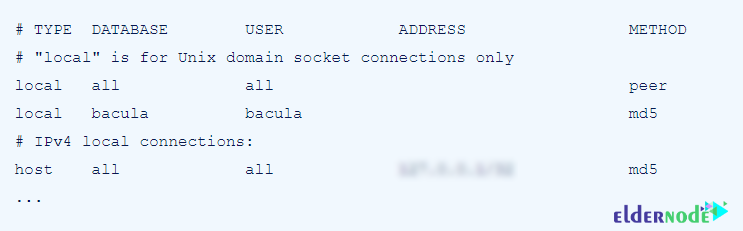
Finally, you must restart the service using the following command to apply the changes:
systemctl restart postgresql.serviceAfter you have successfully installed Postgresql, now we come to the installation of Bacula. The first step is to install the Bacula components using the following commands:
dnf install bacula-director bacula-storage bacula-console bacula-clientYou can create databases, tables, and privileges by following the instructions below. Note that you must run them on behalf of the newly created Bacula user:
cd /usr/libexec/bacula/sudo -u bacula ./create_postgresql_databasesudo -u bacula ./make_postgresql_tablessudo -u bacula ./grant_postgresql_privilegesHow to Configure Bacula on CentOS 8
In this section, we will teach you how to configure Bacula. It should note that you can use the following commands to create any folder to save backups and set bacula as its owner:
mkdir /opt/baculachown bacula:bacula /opt/baculaNext, you need to open the /etc/bacula/bacula-dir.conf file and find the FileSet section called Full Set. Then here, in the Include section, you can set the folders needed for backup. Add /opt/bacula in the Exclude section:
FileSet { Name = "Full Set" Include { ... File = /home/user File = /folder/to/backup } Exclude { File = /opt/bacula … }}After successfully completing the previous step, you should now open the /etc/bacula/bacula-sd.conf file and set Archive Device = /opt/bacula for both Devices:
Device { ... Archive Device = /opt/bacula ... }You can now start the service using the following commands:
systemctl enable --now bacula-dir.servicesystemctl enable --now bacula-fd.servicesystemctl enable --now bacula-sd.serviceNote that the folders specified in the Include section of FileSet are now backed up daily. You can go to the Bacula Management Console using the following command to start the backup:
bconsoleThen enter the run command and follow the instructions. You can use the restore command to recover files. You can also enter status to view scheduled jobs, and then 1. Type help to see all available commands.
Conclusion
Bacula is a suite of computer programs that allow you or the system administrator to technically manage the backup, recovery, and authentication of computer data on a network of different types of computers. Bacula is a network-based backup application. While still on offer, Bacula has many advanced storage management features that make it easy to find lost or damaged files. In this article, we tried to teach you How to Install and Configure Bacula on CentOS 8.