
How to Install Terraform on Windows 10 and windows server 2019. Terraform is an amazing toolset for automating infrastructure in the public and private cloud. Terraform can build, change, and version infrastructure deployed on popular service providers.
This article will walk you through the steps to install Terraform on Windows 10 and Windows Server 2019.
Terraform is a cloud-agnostic Infrastructure automation tool used to manage cloud and on-premise resources in code. With Terraform you can manage Compute, Networking, DNS, Database resources, and many others using simple Declarative Programming Language. See the complete list of Terraform Providers.
Tutorial Install Terraform on Windows 10 / Windows Server
Use the Scoop command-line installer for Windows to setup terraform on Windows.
PS C:\Users\Administrator> scoop install terraform which vim touch WARN Scoop uses 'aria2c' for multi-connection downloads. WARN Should it cause issues, run 'scoop config aria2-enabled false' to disable it. Installing 'terraform' (0.11.12) [64bit] Starting download with aria2 … Download: [#3633c5 96KiB/20MiB(0%) CN:4 DL:245KiB ETA:1m24s] Download: [#3633c5 1.0MiB/20MiB(5%) CN:4 DL:698KiB ETA:28s] Download: [#3633c5 1.7MiB/20MiB(8%) CN:4 DL:688KiB ETA:27s] Download: [#3633c5 2.0MiB/20MiB(10%) CN:4 DL:577KiB ETA:32s] Download: [#3633c5 2.1MiB/20MiB(10%) CN:4 DL:393KiB ETA:47s] Download: [#3633c5 2.4MiB/20MiB(12%) CN:4 DL:384KiB ETA:47s] Download: [#3633c5 2.5MiB/20MiB(12%) CN:4 DL:352KiB ETA:51s] Download: [#3633c5 2.7MiB/20MiB(13%) CN:4 DL:325KiB ETA:55s] .....
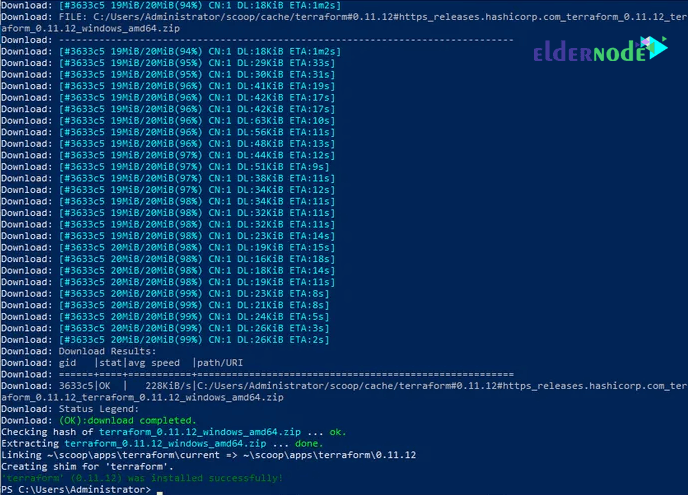
The terraform exe file will be located inside ~ / scoop/ directory.
PS C:\Users\Administrator> which terraform C:\Users\Administrator\scoop\shims\terraform.EXE
How to Configure Terraform on Windows 10 / Windows Server
Now that terraform is installed, let’s create a test project.
> mkdir projects Directory: C:\Users\Administrator Mode LastWriteTime Length Name ---- ------------- ------ ---- d----- 3/9/2019 1:57 AM projects PS C:\Users\Administrator> mkdir projectsCreate a terraform folder inside the projects directory.
PS C:\Users\Administrator> cd .\projects\ PS C:\Users\Administrator\projects> mkdir terraform Directory: C:\Users\Administrator\projects Mode LastWriteTime Length Name ---- ------------- ------ ---- d----- 3/9/2019 1:58 AM terraform PS C:\Users\Administrator\projects> cd .\terraform\Create a Terraform main configuration file.
touch main.tf
I’m doing a Test with AWS Provider but you can use other Providers for your projects.
My terraform configuration provider section is as below:
PS C:\Users\Administrator\projects\terraform> cat .\main.tf # Provider provider "aws" { access_key = "" secret_key = "" region = "us-west-1" }Paste your AWS Access Key and Secret Key inside the access_key and secret_key sections respectively.
When done, run terraform init to initialize a Terraform working directory.
PS C:\Users\Administrator\projects\terraform> terraform init Initializing provider plugins… Checking for available provider plugins on https://releases.hashicorp.com… Downloading plugin for provider "aws" (2.1.0)… The following providers do not have any version constraints in configuration, so the latest version was installed. To prevent automatic upgrades to new major versions that may contain breaking changes, it is recommended to add version = "…" constraints to the corresponding provider blocks in configuration, with the constraint strings suggested below. provider.aws: version = "~> 2.1" Terraform has been successfully initialized! You may now begin working with Terraform. Try running "terraform plan" to see any changes that are required for your infrastructure. All Terraform commands should now work. If you ever set or change modules or backend configuration for Terraform, rerun this command to reinitialize your working directory. If you forget, other commands will detect it and remind you to do so if necessary.
Terraform will automatically download provider configured to .terraform directory.
PS C:\Users\Administrator\projects\terraform> ls Directory: C:\Users\Administrator\projects\terraform Mode LastWriteTime Length Name ---- ------------- ------ ---- d----- 3/9/2019 2:06 AM .terraform -a---- 3/9/2019 2:04 AM 42358 .main.tf.un~ -a---- 3/9/2019 2:04 AM 99 main.tf -a---- 3/9/2019 2:03 AM 59 main.tf~Inside there is another folder which store plugins downloaded by Terraform.

Let’s now add resource section to create AWS VPC and Subnet resources by editing the main.tf file.
# Provider provider "aws" { access_key = "" secret_key = "" region = "" } # Retrieve the AZ where we want to create network resources data "aws_availability_zones" "available" {} # VPC Resource resource "aws_vpc" "main" { cidr_block = "10.11.0.0/16" enable_dns_support = true enable_dns_hostnames = true tags { Name = "Test-VPC" } tags { Environment = "Test" } } # AWS subnet resource resource "aws_subnet" "test" { vpc_id = "${aws_vpc.main.id}" cidr_block = "10.11.1.0/24" availability_zone = "${data.aws_availability_zones.available.names[0]}" map_public_ip_on_launch = "false" tags { Name = "Test_subnet1" } }Save the file after adding resource definitions and setting AWS variables then generate and show an execution plan.
PS C:\Users\Administrator\projects\terraform> terraform plan Refreshing Terraform state in-memory prior to plan... The refreshed state will be used to calculate this plan, but will not be persisted to local or remote state storage. data.aws_availability_zones.available: Refreshing state... ------------------------------------------------------------------------ An execution plan has been generated and is shown below. Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols: + create Terraform will perform the following actions: + aws_subnet.test id: <computed> arn: <computed> assign_ipv6_address_on_creation: "false" availability_zone: "us-east-1a" availability_zone_id: <computed> cidr_block: "10.11.1.0/24" ipv6_cidr_block: <computed> ipv6_cidr_block_association_id: <computed> map_public_ip_on_launch: "false" owner_id: <computed> tags.%: "1" tags.Name: "Test_subnet1" vpc_id: "${aws_vpc.main.id}" + aws_vpc.main id: <computed> arn: <computed> assign_generated_ipv6_cidr_block: "false" cidr_block: "10.11.0.0/16" default_network_acl_id: <computed> default_route_table_id: <computed> default_security_group_id: <computed> dhcp_options_id: <computed> enable_classiclink: <computed> enable_classiclink_dns_support: <computed> enable_dns_hostnames: "true" enable_dns_support: "true" instance_tenancy: "default" ipv6_association_id: <computed> ipv6_cidr_block: <computed> main_route_table_id: <computed> owner_id: <computed> tags.%: "2" tags.Environment: "Test" tags.Name: "Test-VPC" Plan: 2 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy. ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Note: You didn't specify an "-out" parameter to save this plan, so Terraform can't guarantee that exactly these actions will be performed if "terraform apply" is subsequently run. PS C:\Users\Administrator\projects\terraform>Finally build your Infrastructure with Terraform using terraform apply.
PS C:\Users\Administrator\projects\terraform> terraform apply data.aws_availability_zones.available: Refreshing state... An execution plan has been generated and is shown below. Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols: + create Terraform will perform the following actions: + aws_subnet.test id: <computed> arn: <computed> assign_ipv6_address_on_creation: "false" availability_zone: "us-east-1a" availability_zone_id: <computed> cidr_block: "10.11.1.0/24" ipv6_cidr_block: <computed> ipv6_cidr_block_association_id: <computed> map_public_ip_on_launch: "false" owner_id: <computed> tags.%: "1" tags.Name: "Test_subnet1" vpc_id: "${aws_vpc.main.id}" ...........................Confirm changes to be made and type yes to initiate modifications.
Plan: 2 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy. Do you want to perform these actions? Terraform will perform the actions described above. Only 'yes' will be accepted to approve. Enter a value: yes
A successful terraform run should print success message at the end.
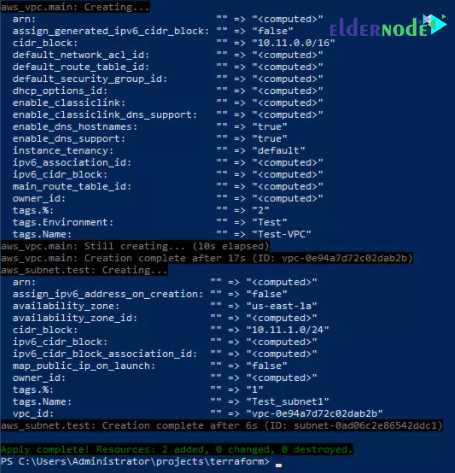
Terraform state is saved to .\terraform.tfstate but the backend can be changed.
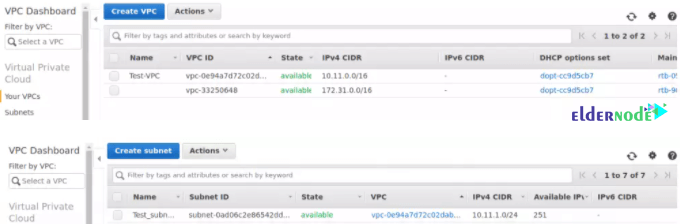
Note: You can confirm Infrastructure changes from AWS console.
How to Destroy Terraform Infrastructure
We have confirmed that our Terraform installation on Windows is working as expected.
Destroy Terraform-managed infrastructure by running terraform destroy command.
PS C:\Users\Administrator\projects\terraform> terraform destroy aws_vpc.main: Refreshing state... (ID: vpc-0e94a7d72c02dab2b) data.aws_availability_zones.available: Refreshing state... aws_subnet.test: Refreshing state... (ID: subnet-0ad06c2e86542ddc1) An execution plan has been generated and is shown below. Resource actions are indicated with the following symbols: - destroy Terraform will perform the following actions: - aws_subnet.test - aws_vpc.main Plan: 0 to add, 0 to change, 2 to destroy. Do you really want to destroy all resources? Terraform will destroy all your managed infrastructure, as shown above. There is no undo. Only 'yes' will be accepted to confirm. Enter a value: yes
Note: If you don’t want confirmation prompt, use the following command:
terraform destroy -auto-approve

Login to AWS console and affirm resources deletion.
Goodluck.




