
In the world of web hosting, various web servers are used, one of the most widely used of which is Apache. However nowadays, alternatives such as Nginx and LiteSpeed have been added, both of which are rapidly taking over the market. In this article, we will compare LiteSpeed vs Nginx vs Apache and you will learn about their technologies and features to conclude Which Is the Best Web Server. You can visit the packages available in Eldernode to purchase a VPS Server.
Table of Contents
LiteSpeed vs Nginx vs Apache: Which Is the Best Web Server?
What is a Web Server?
A web server is a computer software that is a subset of the server and has the task of storing information and sending the content of a website to the client. The most common type of client is browsers. When you load a site or click a link to download a file, the browser is sending your request to that website’s web server.
In terms of hardware, the web server is like a computer that stores website files such as CSS sheets, images, JavaScript, and HTML files. The web server sends the data stored on the server to the users via internet.
Examining the web server in terms of software shows that its different parts control the access method of users. For example, the HTTP server software first checks the request to display the site through the http protocol and sends the correct response according to it.
In the following, we will compare 3 of the most widely used web servers in terms of speed, architecture, configuration, compatibility with the operating system, etc.
Introduction to Apache
Apache is a reliable and open-source web server that has been available since 1995. Apache is very easy to setup and running, as it comes pre-installed on all major Linux distributions.
Introduction to Nginx
Nginx was created in 2004 with the aim of outperforming the Apache web server. Nginx server only static files, consumes much less memory than Apache and can handle more requests per second compared to Apache.
Introduction to LiteSpeed
LiteSpeed is one of the newest web servers. With LiteSpeed’s simple architecture and high performance, users who run it can double the capacity of websites on their servers (Assuming they were already running Apache).
You can see the comparison of 3 web servers in terms of usage for websites in the image below:
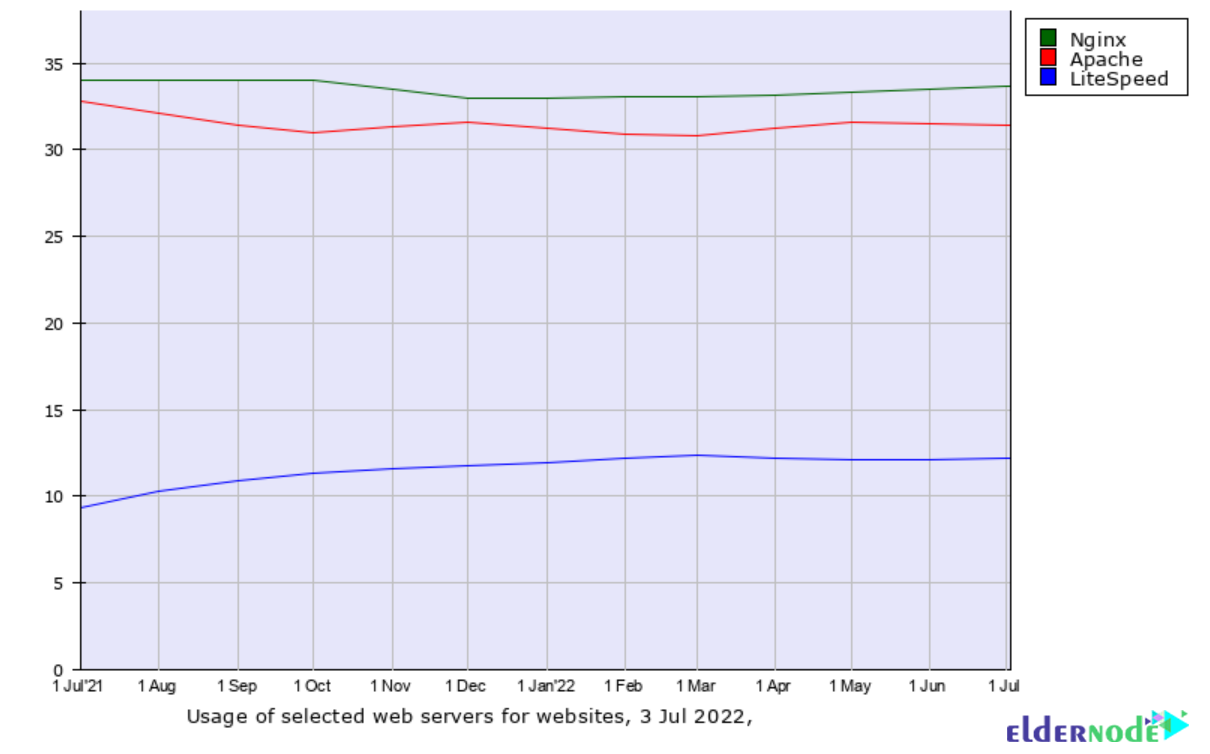
Comparison of Web Servers in Terms of Architecture
–> The architecture in Apache is process-based; There is a main process that creates a new process when each new HTTP request is received. In this case, due to the high number of processes, your memory usage may increase exponentially during peak hours.
–> Nginx has an event-driven architecture; with each incoming HTTP request, a new event is generated. In this case, there is a main process that oversees the entire server and performs the main tasks, and several assistant processes that distribute the server’s operational tasks between them. Due to workload division, these architecture are much lighter and more efficient. Your memory usage doesn’t change much during peak hours.
–> The architecture in LiteSpeed, like the architecture of Nginx, is event driven.
Comparison of Web Servers in Terms of Speed
Apache uses more memory and usually has a longer response time during peak hours. Nginx is faster than Apache, but LiteSpeed is faster than both.
According to the LiteSpeed team’s tests, the WordPress instances for each of the three web servers are as follows:
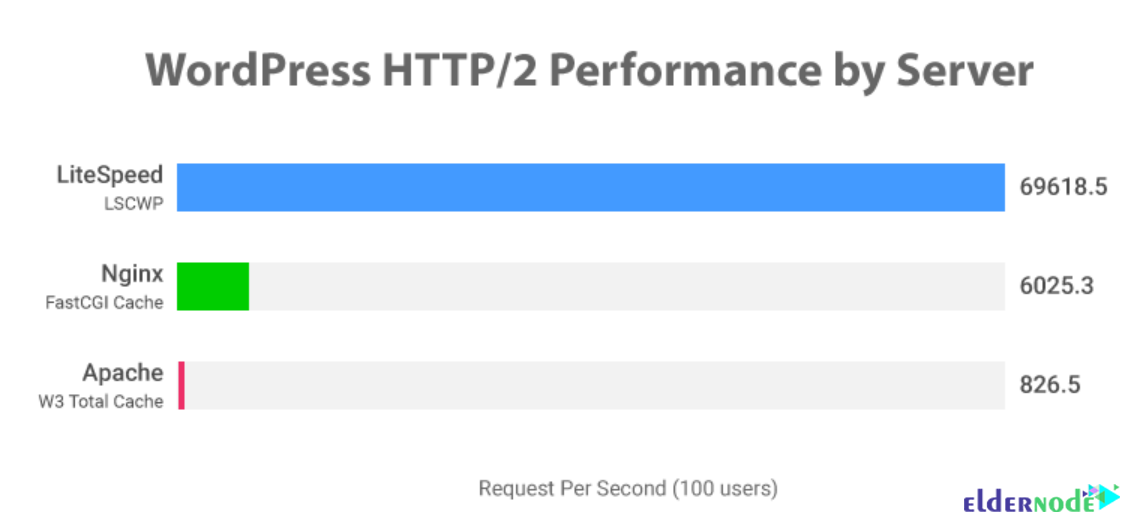
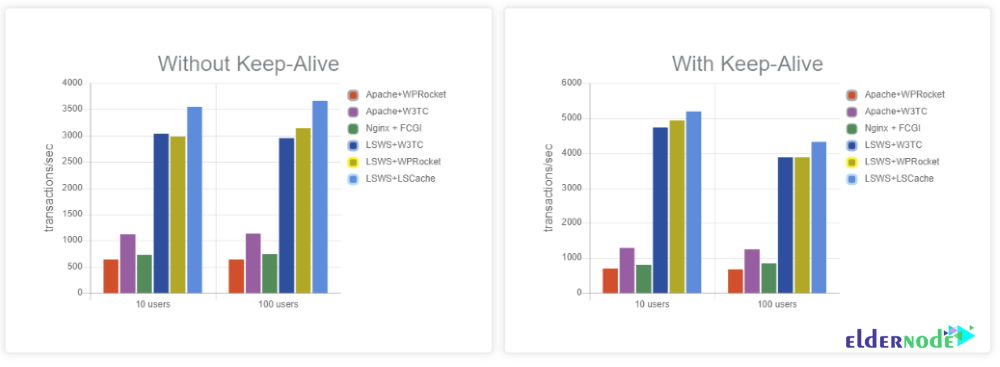
Next you can see the chart of LiteSpeedtech that shows the amount of transactions per second with and without Keep-Alive:
Comparison of Web Servers in Terms of Caching
A web server cache is a software that stores web pages and accessible resources. In the following, you can see how a web server works with cache enabled:
1–> Sending HTTP request to the server by the browser.
2–> If the requested data exists in the cache, the cache intercepts the request and responds to it.
3–> If there is no requested data in the cache, the web server will respond to request. Note that if data matches the configured storage filters, the cache stores them.
The above process, reduces the server workload, increases the overall performance and bandwidth of the website and reduces the loading time of the web page.
–> Apache has different cache modules such as mod_cache, mod_cache_disk, mod_file_cache and htcacheclean. This way you can access preloading files into memory at startup, implementing hidden storage filters, and server-wide key-value based object storage.
–> You can enable Nginx cache through cPanel. Nginx cache features: The ability to add multiple users to the cache, force cache expiration after configuration time, and change the default cache location.
–> LiteSpeed features: Server-side caching, ability to cache private and public dynamic content on the same page, and integration with Quic.Cloud CDN. Quic.Cloud CDN caches static and dynamic WordPress content.
Note: LiteSpeed cache plugins are available for various web applications such as WordPress, OpenCart, XenForo, Laravel, MediaWiki, etc.

Comparison of Web Servers in Terms of OS Supports
Apache: Supports for all Unix operating systems (CentOS, Redhat, Fedora, etc.) and MS Windows.
Nginx: Supports all Unix and Windows operating systems.
LiteSpeed: Supports CentOS 7+, Ubuntu 14.04+, Debian 8+, FreeBSD 9+ and Linux Kernel 3.0+.
Comparison of Web Servers in Terms of Configuration
–> Apache’s .htaccess file helps you implement redirects, password protection, custom error messages, indexing, etc.
–> The conf. files in Nginx control items like the number of worker threads, exposed ports, load balancing, redirects ,etc.
–> You can configure LiteSpeed through an Intuitive GUI, such as creating listeners, opening Firewall ports, implementing redirects, and reading Apache .htaccess files.
Comparison of Web Servers in Terms of Security
Modsecurity rules run on all three web servers and protect your system against some of the most common DDoS attacks.
Apache, with its proven security, quickly fixes any security issues that may arise. It also protects against DDoS attacks and score increase with different configuration parameters.
Nginx has a relatively secure design, making Nginx deployments secure.
LiteSpeed provides security with reCAPTCHA support, protection against WordPress brute-force attacks, and other DDoS protection features.
Comparison of Web Servers in Terms of Compatibility with the Control Panel
Apache compatible control panels: cPanel, Kloxo, Ajenti, OpenPanel, ZPanel, etc.
Nginx compatible control panels: cPanel, aaPanel, Vesta, Hestia CP, etc.
LiteSpeed compatible control panels: cPanel, Plesk, Direct Admin, CyberPanel, Cloud Pages.
Comparison of Web Servers in Terms of Plugins
Apache: Hosts third-party modules and provides features such as SQL connection management, data compression, CGI script execution, etc.
Nginx: Providing third-party modules and features such as HTTP digest authentication, dynamic IP locking, etc.
LiteSpeed: It has multiple control panel and cache plugins along with an API, so it makes it easy for developers to integrate with third-party apps:

Comparison in Terms of Script Language Support
Apache: Supports for different languages like PHP, Python and Perl using third-party modules like mod_php, mod_python, and mod_perl etc.
Nginx: Supports for 7 languages such as Go, JavaScript, Perl, PHP, Python, Ruby and Java servlet containers (as a test module).
LiteSpeed: Supports for all programming languages including Perl, PHP, Python, Ruby and Java.
Comparison of Web Servers in Terms of Supporting HTTP3
Apache: It doesn’t have HTTP3 support.
Nginx: After previewing its HTTP3 support in 2020, Nginx released the feature roadmap in July 2021.
LiteSpeed: It has strong and reliable support for HTTP3.
Comparison of Web Servers in Terms of CMS Integrations
Apache: Running WordPress, Joomla, Drupal, Magento, etc.
Nginx: Running WordPress, Joomla, Drupal, Magento, PrestaShop, etc.
LiteSpeed: Compatible with WordPress, Joomla, Drupal, Magento, PrestaShop, OpenCart, Shopware, MediaWiki.
FAQ
[sp_easyaccordion id=”38148″]
Conclusion
In this article, we got acquainted with three cases of practical web servers and compared these web servers from various aspects such as architecture, configuration, plugins, speed, etc. I hope that by reading this article, you can choose the best web server that is compatible with your needs.




