
NTP stands for Network Time Protocol and is using to fine-tune and synchronize the clocks of systems and devices with atomic clocks. NTP servers follow a hierarchical structure called Stratum. This protocol uses the UDP 123 port and allows the network device to synchronize their time. Ideally, these devices should synchronize their time with a trusted server. You can configure your router to act as an NTP server for the local network. On the other hand, this router must be another NTP server on the Internet or another access point as the NTP Client to synchronize its time with it. In this article, we try to learn How to Install NTP server on Fedora. You can also visit the packages available in Eldernode to purchase a VPS server.
Table of Contents
Tutorial Install NTP server on Fedora 33
Network Time Protocol is a default algorithm used to synchronize the operating time of an operating system. This protocol has fault tolerance. It is also a protocol that performs time unification based on a specific and designed time source. Time Synchronization for the NTP protocol is performing over a period of time and involves the transmission of NTP packets. NTP packets contain a timestamp, which is like a label that contains a time pattern of the user and a pattern of the participating server.
NTP relies on a clock source to set the time for the rest of the system to specify a universal time. This protocol uses UTC (Coordinate Universal Time) as the exact source of the time standard. UTC enables the NTP algorithm to be used worldwide regardless of time zone settings. Time Zones is the geographical division of the world into 15 parts, starting from Greenwich in England and its job is to show the clocks of different regions of the world.
How does NTP work?
There are thousands of NTP servers around the world that have access to Atomic Clocks and GPS clocks services. If we intend to equip any computer with one of these servers, it does not make sense and it is not financially viable. But by implementing the NTP protocol, you can create this synchronization. For example, in the Windows version, this feature is available but is not enabled by default.
NTP client requests time exchange with NTP server. As a result of this exchange, the customer is able to calculate the link delay and local offset and set his own local clock to match the clock on the server. As a rule, six exchanges in about 5 to 10 minutes are required to determine the initial time. After synchronization, the NTP client updates every 10 minutes, usually requiring only one message exchange. This transaction is done through port 123 of the UDP protocol.
NTP features (In article Install NTP server on Fedora 33)
1. NTP provides a reference clock that acts as a fixed point for all synchronization processes. All clocks are synchronizing according to this time. From the beginning, Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), known as a uniform global clock, was used for this purpose.
2. NTP is a protocol that automatically searches for the best time sources for synchronization. Multiple sources can combine to minimize any accumulation of errors in coordination. Where possible, the network time protocol detects and ignores time sources that provide temporarily or permanently very strong deflection values.
3. NTP is highly scalable. Each sync network may have several reference hours. In addition, each network node is able to transmit time information in a two-way (point-to-point) or one-way hierarchical structure.
4. NTP is very accurate. Thanks to the possibility of choosing the best synchronization candidate, the right result is possible up to one nanosecond.
5. NTP can fix temporary network connection problems.
In the continuation of this article, join us in learning how to Install the NTP server on Fedora.
Install NTP server on Fedora
In this section, we try to teach you how to install an NTP server using NTPd on Fedora. Follow us in this tutorial to set up your NTP server to set the time automatically. Since the NTP daemon is provided by the NTP package, you must use the following command to install NTPd:
dnf install ntp -yNext, to use NTPd from the user’s default space daemon, chronyd, must be stopped and disabled. Therefore, you should use the following commands to stop and disable Chronyd from restarting the system.
systemctl stop chronydsystemctl disable chronydAfter executing the above commands, you should now use the following commands to start and enable NTPd when starting the system:
systemctl start ntpdsystemctl enable ntpdHow to Configure NTP server on Fedora
Note that the main configuration file for NTP is /etc/ntp.conf. It should note that this configuration file is installing with NTPd and is configuring by default to use time servers from the Fedora pool.
You can configure or restrict access to the NTP service using the restrict command in the ntp.conf file to configure NTP service access control. You can also edit /etc/ntp.conf using the following command to restrict local access to the server. By doing this, you can add the domain of the network from which the server is allowed to receive the request.
vim /etc/ntp.conf
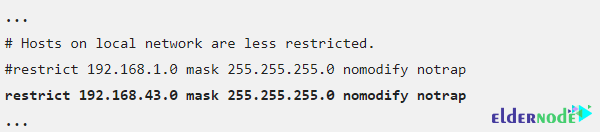
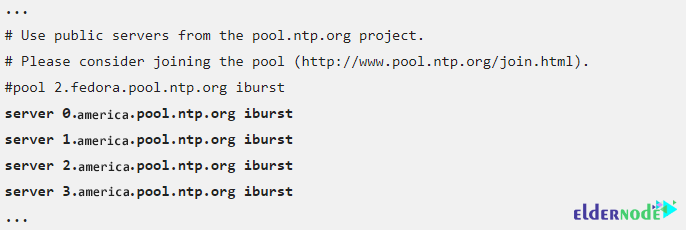
You can also configure time servers. It should note that NTP is configured by default to use time servers from the Fedora pool. You can easily change this by replacing time servers with servers close to your area.
Conclusion
There are thousands of NTP servers around the world that have access to Atomic Clocks and GPS clocks services. If we intend to equip any computer with one of these servers, it does not make sense and it is not financially viable. You can create this synchronization by implementing the NTP protocol. In this article, we tried to learn how to Install the NTP server on Fedora. You can refer to these articles if you want to install and configure NTP Server on Ubuntu, CentOS, and Debian.




