
[Updated on Date: 2021-01-16] MongoDB is a popular document-based and general-purpose NoSQL database engine that stores data in JSON format. The MongoDB is free and open-source and ships with a set of cool and nifty features such as file storage, data replication, Ad-hoc queries, and load balancing just to mention a few. Some of the blue-chip companies that have incorporated MongoDB in their applications include Adobe, Facebook, Google, eBay, and Coinbase. In this article, we are going to learn you How To Install MongoDB 4 In CentOS 8. You can visit the packages available in Eldernode to purchase a CentOS VPS server.
Table of Contents
Tutorial Install MongoDB 4 In CentOS 8
In this article, you will learn How to install MongoDB 4 in CentOS 8. Join us to check the details.
How To Add MongoDB Repository
Since MongoDB is not present in the CentOS 8 default repository, you need to add it manually. So firstly, create a repository file as shown.
vi /etc/yum.repos.d/mongodb.repo Paste the configuration below and save the file.
[mongodb-org-4.2] name=MongoDB Repository baseurl=https://repo.mongodb.org/yum/redhat/$releasever/mongodb-org/development/x86_64/ gpgcheck=1 enabled=1 gpgkey=https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-4.2.ascInstall MongoDB in CentOS 8 | CentOS 7
Once the repository enabled, you can install MongoDB using the following dnf command:
dnf install mongodb-orgThen, start and enable MongoDB to start on boot by running the commands below:
systemctl start mongod sudo systemctl enable mongodUse the following command to verify the status of MongoDB:
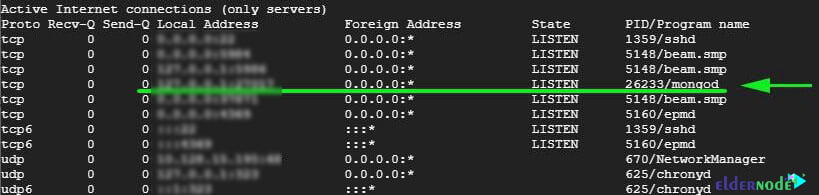
systemctl status mongod And also, to confirm that indeed Mongod service is listening:
netstat -pnltu
How To Access MongoDB Shell
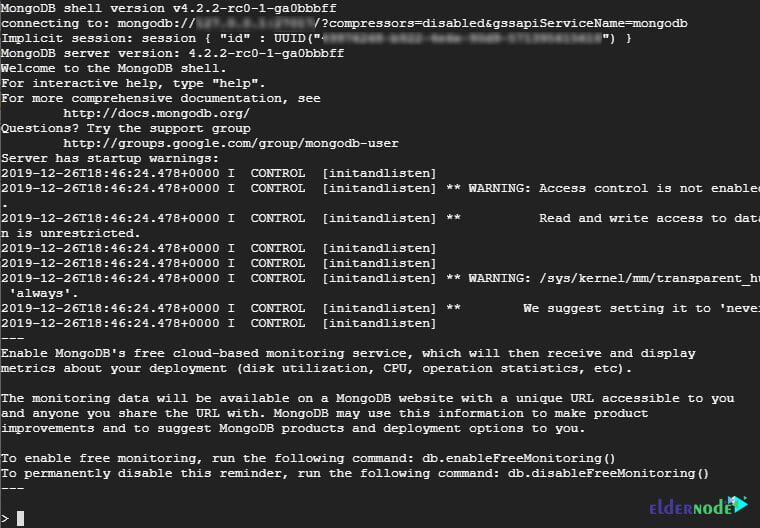
It is time to access MongoDB’s shell by simply issuing the command:
mongoThe output will be similar to the below screenshot
How To Create MongoDB Admin User
Let’s now switch gears and create an Admin user. It’s always good advice to create an admin user with elevated privileges to perform elevated tasks. To do so, first access MongoDB’s shell:
mongoTo switch to the database admin, type the command below.
> use admin Now, create a new MongoDB user by running the code below.
> db.createUser( { user: "mongod_admin", pwd: "P@ssword@2019", roles: [ { role: "userAdminAnyDatabase", db: "admin" } ] } You will get the output below when all is ok.
Successfully added user: { "user" : "mongod_admin", "roles" : [ { "role" : "userAdminAnyDatabase", "db" : "admin" } ] } 
Next, run the following command to list MongoDB users created.
show users How To Configure Authentication for MongoDB
As you see, all users can access the shell and execute any commands, which is not recommended at all for security purposes. So you need to create authentication for the admin user we just created so as to prevent other users from running commands without authorization.
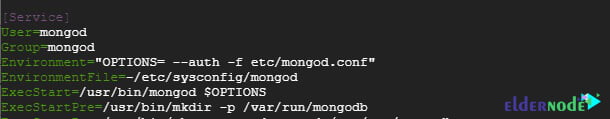
To enable authentication to edit the /lib/systemd/system/mongod.service file, under the [Service] section, locate and edit the Environment parameter as shown:
Environment="OPTIONS= --auth -f /etc/mongod.conf"
Now, you can save and exit the configuration file.
For the changes to come into effect, reload the system and restart MongoDB.
systemctl daemon-reloadsystemctl restart mongodIf you now try listing the users without authentication, you should get an error as shown:

To authenticate, simply pass the credentials as shown.
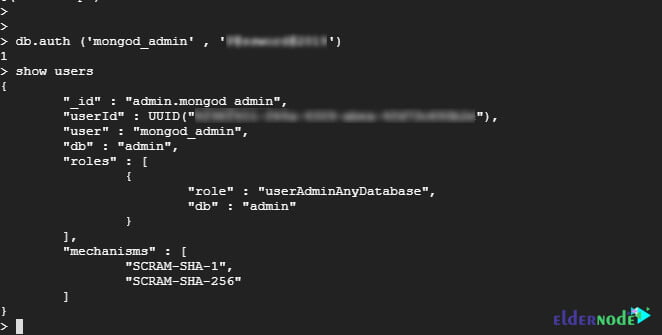
> db.auth('mongod_admin', 'P@ssword@2019') Now you can run any command after that. Let’s try listing the users once more:
> show usersThis time, all went well since the authentication credentials were provided.
Run the command below to exit the database engine:
exitConclusion
In this article, you succeeded to learn How to install MongoDB 4 in CentOS 8, and from now on we hope you are comfortable installing MongoDB4 on your CentOS 8 system and getting started with a few necessary steps. You can refer to the articles How to install MongoDB 4 on Debian 10 and How to install MongoDB on Windows.





What if we need to manage its service?
You can manage the MongoDB service by running the following command:
sudo systemctl status mongodNote: When you see ‘’inactive’’ in the output, It means MongoDB service is not running. To ensure that MongoDB service is automatically starting on system boot, you must see the ‘’enable’’ in output.
thank you. After starting the MongoDB service, I received an error that the unit is not found.
– In this situation, run the following command and then the second one (start MongoDB)
sudo systemctl daemon-reloadsudo systemctl start mongodis it possible to stop MongoDB?
Yes it is. Stop the MongoDB process by running the command below:
sudo systemctl stop mongodgood tutorial.i wanna remove packages and data. thanks
You can use the following command to remove all packages you have installed.
sudo yum erase $(rpm -qa | grep mongodb-org)And also to remove MongoDB database and log file run the commands below:
sudo rm -r /var/log/mongodbsudo rm -r /var/lib/mongo
I need to undo uninstalling MogoDB.
Unfortunately it is not possible. The process you have done removed the configuration, and all databases. So this is not reversible. Next time, ensure back up all of your configuration and data before proceeding.