Managing Linux servers can be very difficult at times. You can manage your server easily with the help of control panels like Webmin. Webmin offers extensive functionality that allows you to effectively manage your server through a user-friendly web interface. This article will teach you How to Manage the Server with Webmin. If you intend to buy Linux VPS servers, you can check out the packages offered on the Eldernode website.
Table of Contents
What is Webmin and Its Features?
Webmin is a web-based system administration tool that provides a graphical user interface for managing Unix-like systems. You can perform various system administration tasks without having to use the command line interface. It allows you to manage various aspects of your server through a graphical user interface. Here are some of the main features of Webmin:

System Configuration
Webmin allows administrators to configure and manage various system settings such as network configuration, disk quotas, file system, user accounts, services, and more. It provides an intuitive interface to modify system parameters without the need for manual configuration files.
User and Group Management
Webmin allows administrators to create, modify, and delete user accounts and groups. It also provides options to manage user privileges, password policies, and access control.
Server Management
With Webmin, administrators can manage different types of servers like web servers (Apache, Nginx), database servers (MySQL, PostgreSQL), mail servers (Sendmail, Postfix), and file servers (Samba). It provides tools to configure server settings, monitor server status, and perform necessary administrative tasks.
System Monitoring
Webmin offers monitoring capabilities to keep track of system performance, resource usage, and network activity. It provides real-time graphs and statistics to analyze system health, identify bottlenecks, and troubleshoot issues.
File Management
Through Webmin, administrators can navigate and manage files and directories on the system. They can perform basic file operations like creating, deleting, copying, and moving files. It also supports file and folder permissions management.
Software Package Management
Webmin provides tools to manage software packages on the system. It supports package managers like APT and YUM to install, update, and remove software packages. Administrators can browse available packages, search for specific software, and perform package-related tasks.
Firewall Configuration
Webmin includes a firewall management module that allows administrators to configure and manage firewall rules. It supports popular firewall solutions like iptables and firewalld, enabling administrators to control network traffic and enhance system security.
Backup and Restore
Webmin offers backup and restore capabilities to protect system data. Administrators can schedule automated backups, specify backup destinations, and restore data when needed. It supports various backup methods, including local backups, remote backups, and incremental backups.
DNS and DHCP Management
Webmin provides modules for managing DNS and DHCP services. Administrators can configure DNS zones, add DNS records, and manage DNS settings. They can also manage DHCP leases, define DHCP options, and monitor DHCP server activity.
SSL Certificate Management
Webmin includes tools for managing SSL certificates. Administrators can generate certificate signing requests (CSRs), install SSL certificates, and configure SSL/TLS settings for web servers and other services.
Benefits of Using Webmin for Server Management
Using Webmin for server management offers several benefits for administrators. Here are some of the key advantages:
User-Friendly Interface
Webmin provides a web-based graphical user interface (GUI) that makes server management tasks more accessible and intuitive. Administrators can perform a wide range of system configuration and management tasks using a familiar web browser, without the need for extensive command-line knowledge.
Centralized Management
With Webmin, administrators can centrally manage multiple servers from a single interface. They can easily switch between different servers and perform common administrative tasks without needing to log in to each server individually. This centralized approach saves time and effort, especially in environments with multiple servers.
Platform Independence
Webmin is a platform-independent tool that can be used to manage various Unix-like systems, including Linux, BSD, and macOS. It provides a consistent interface across different platforms, allowing administrators to manage servers running on different operating systems using the same tool.
Extensibility
Webmin is highly extensible and supports a wide range of modules and plugins. Administrators can add additional functionality to Webmin by installing modules specific to their needs. These modules can extend the capabilities of Webmin and provide additional tools for managing specific services or applications.
Enhanced Security
Webmin includes built-in security features to enhance server security. It supports SSL encryption for secure communication between the browser and the Webmin server, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data. Additionally, Webmin allows administrators to control user access and permissions, ensuring that only authorized users can perform specific actions.
Time-Saving Automation
Webmin allows administrators to automate repetitive tasks through its scheduling and automation features. They can schedule backups, software updates, and other routine tasks to run automatically at specified intervals, reducing manual effort and ensuring consistent system maintenance.
Community Support
Webmin has a large and active community of users and developers. Administrators can benefit from the community’s knowledge and support by accessing forums, documentation, and user-contributed modules. The community provides a valuable resource for troubleshooting issues, sharing best practices, and staying up to date with the latest developments in Webmin.
Cost-Effective Solution
Webmin is an open-source tool that is available free of charge. It provides powerful server management capabilities without the need for expensive proprietary software. This makes it a cost-effective solution for organizations looking to manage their servers efficiently without incurring additional licensing costs.
Installing and Setting up Webmin
The Webmin project provides a repository for Debian and RHEL/CentOS-based systems. Let’s see how can you install Webmin on your server.
RHEL/CentOS:
If you are using RHEL/CentOS, you should first add it to the list of yum repositories as follows:
cat << EOM | sudo tee /etc/yum.repos.d/webmin.repo [Webmin] name=Webmin Distribution Neutral baseurl=http://download.webmin.com/download/yum enabled=1 gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=http://www.webmin.com/jcameron-key.asc EOMNow install Webmin using the following command:
sudo yum install webminUbuntu/Debian:
But if you are using Debian-based systems, you should add it to the apt list:
echo "deb http://download.webmin.com/download/repository sarge contrib" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/webmin.listAdd Jamie Cameron’s PGP key using the command below:
wget -qO - http://www.webmin.com/jcameron-key.asc | sudo apt-key add -This will allow apt to verify the packages.
Now you can install Webmin with the following command:
sudo apt updatesudo apt install webminNavigating the Webmin Interface
Open a web browser and enter the URL or IP address of your Webmin server:
https://<your_server_ip>:10000/You will be presented with the login page. Enter your username and password to log in. Make sure you have the necessary credentials from your administrator:
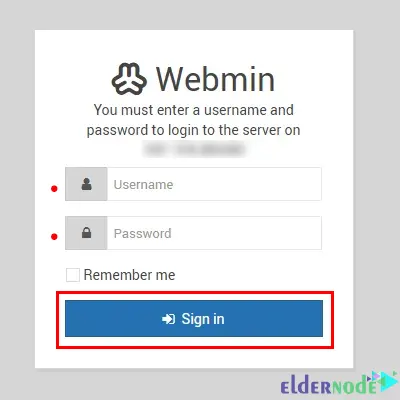
After logging in, you will be taken to the Webmin dashboard. The dashboard provides an overview of system information, such as CPU usage, memory usage, disk usage, and network activity. It may also display quick links to commonly used features.
Managing Users and Permissions with Webmin
Webmin offers many functions in the form of modules. There are modules for server management.
Packages Management
This module allows you to easily install and remove packages from Webmin. Go to System >> Software packages from the left column. The exact details shown on the following page will vary depending on the distribution you are running Webmin on:
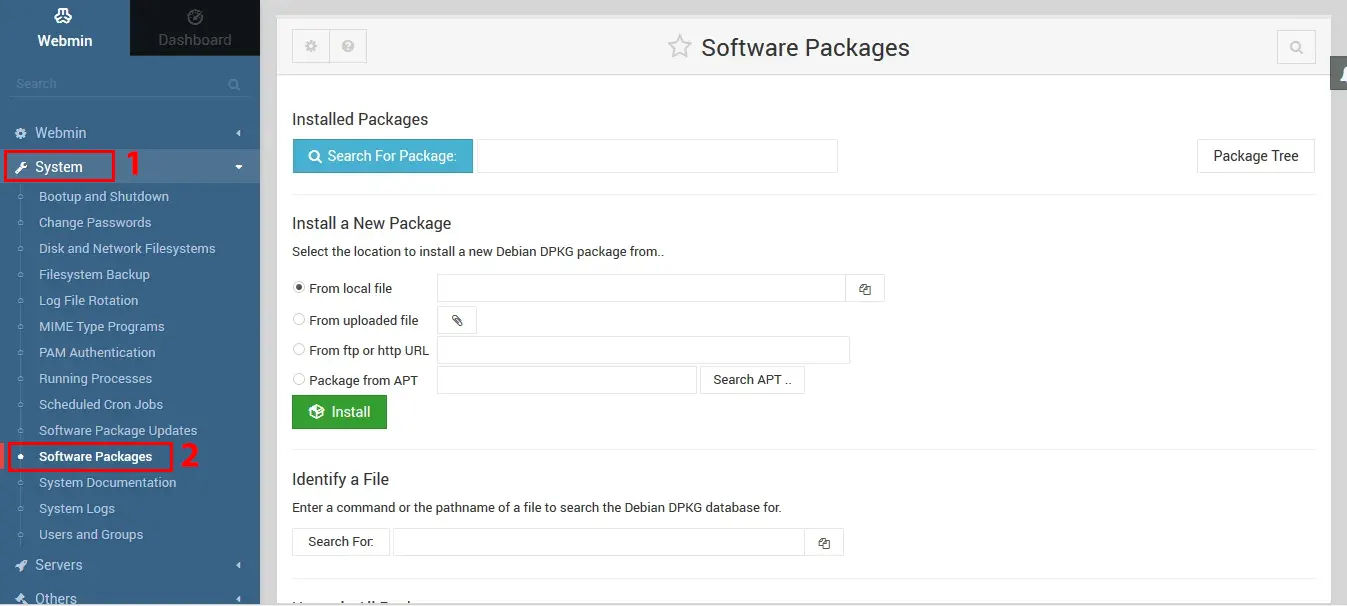
From this section, you can install a package using apt or from a local or remote package file, search for a package installed on your system and see more information about it, or remove it.
To update packages, go to the System >> Software Package Updates from the left menu. Or simply click the “package update is available” notification on the dashboard to go to the “Software Package Updates” page:
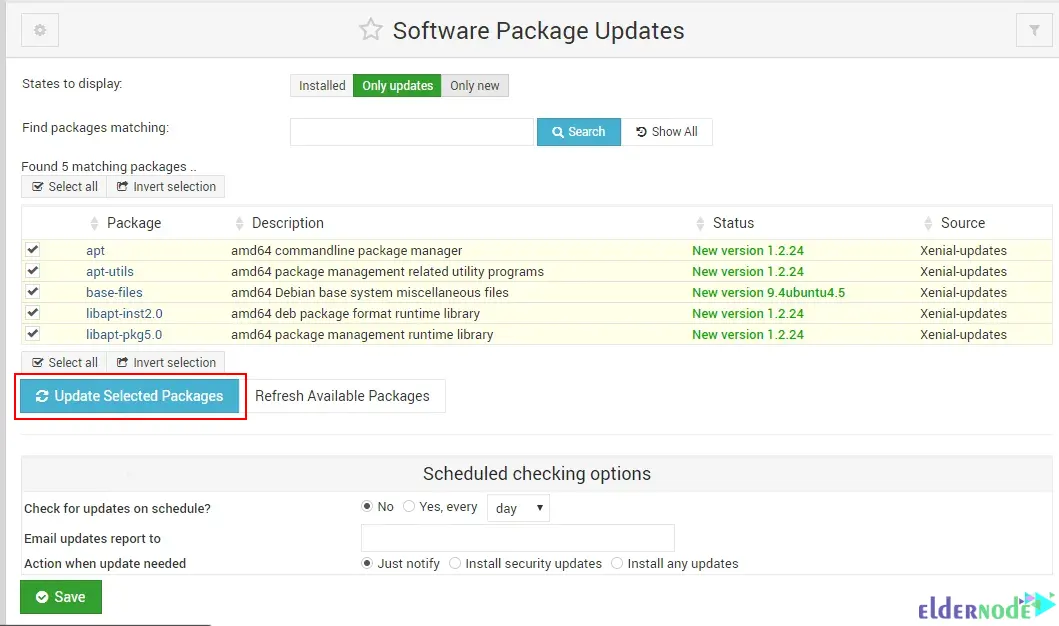
Also to update the individual packages, just choose them and click “Update Selected Packages”. The Scheduled checking options section allows you to configure automatic updates.
Users Management
The user configuration option allows you to easily add or remove users from your system. From the left menu, navigate to Webmin >> Webmin Users >> Create a new Webmin user path:
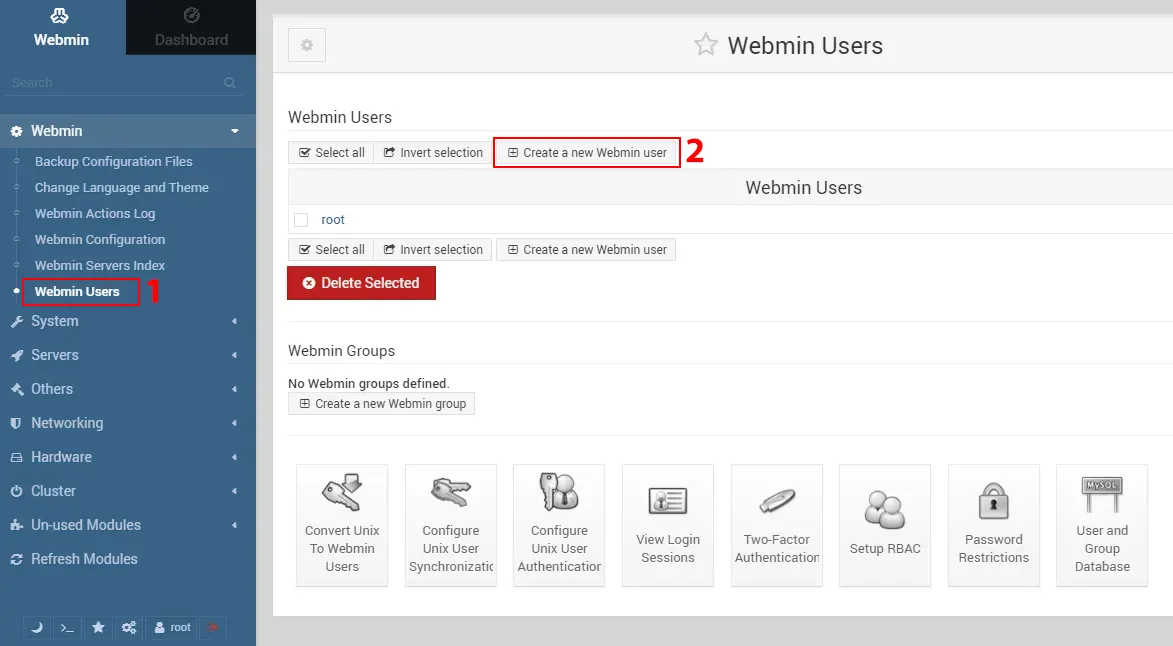
To remove a user, just choose the user by clicking on the checkbox and then delete them with the “Delete selected” button.
File Manager
Webmin is a simple web-based file manager that allows you to browse, upload and download files. You can go to Others >> File Manager from the main menu to open it:
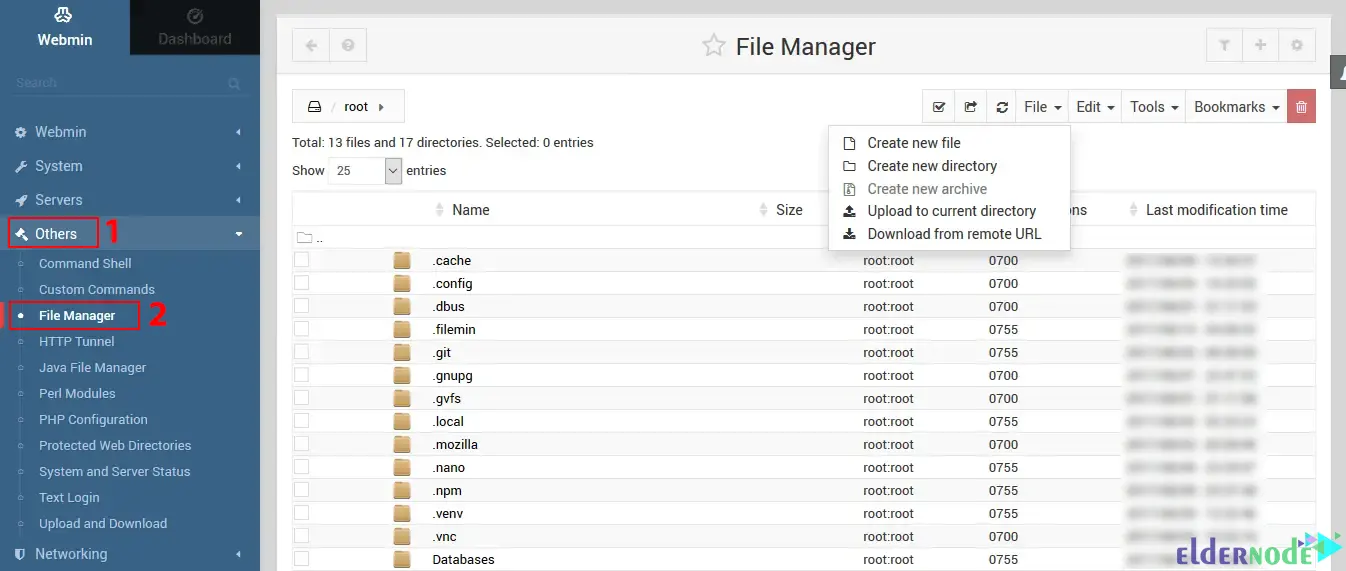
You can create a new file or upload a file using the ”File” menu on the top right. Also, the ”Tools” menu allows you to perform advanced tasks like changing file permissions.
Command-line Shell
Webmin also provides a command line shell that you can open from Others >> Command Shell. This command line is fine for some quick command-line-based tasks, but interactive programs may not run.
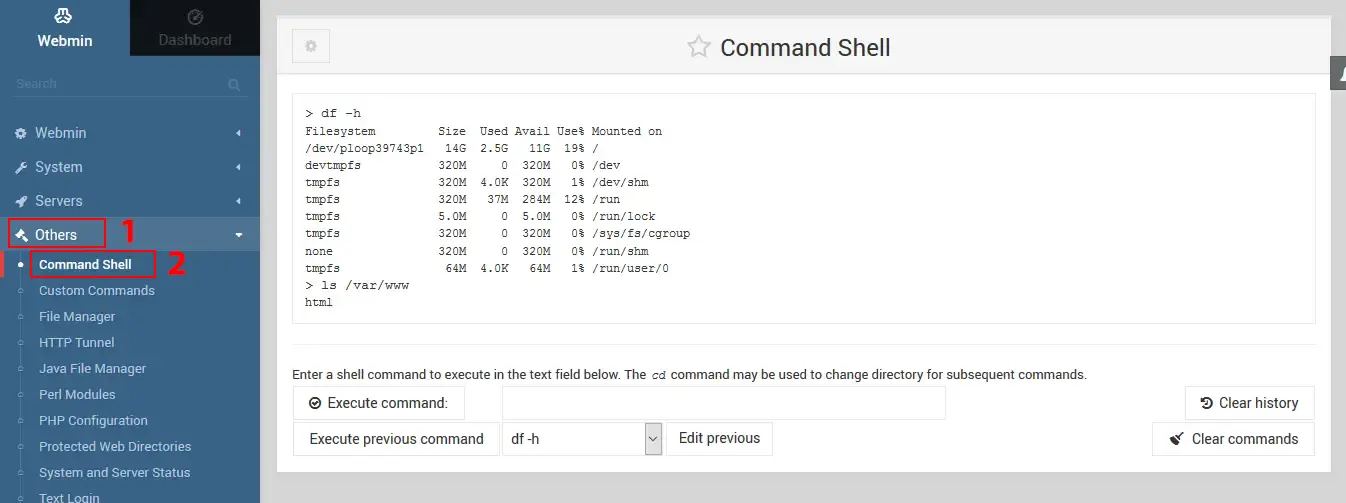
Webmin Configuration
Webmin provides a wide variety of configuration options. Click on Webmin >> Webmin Configuration from the left menu to access them:
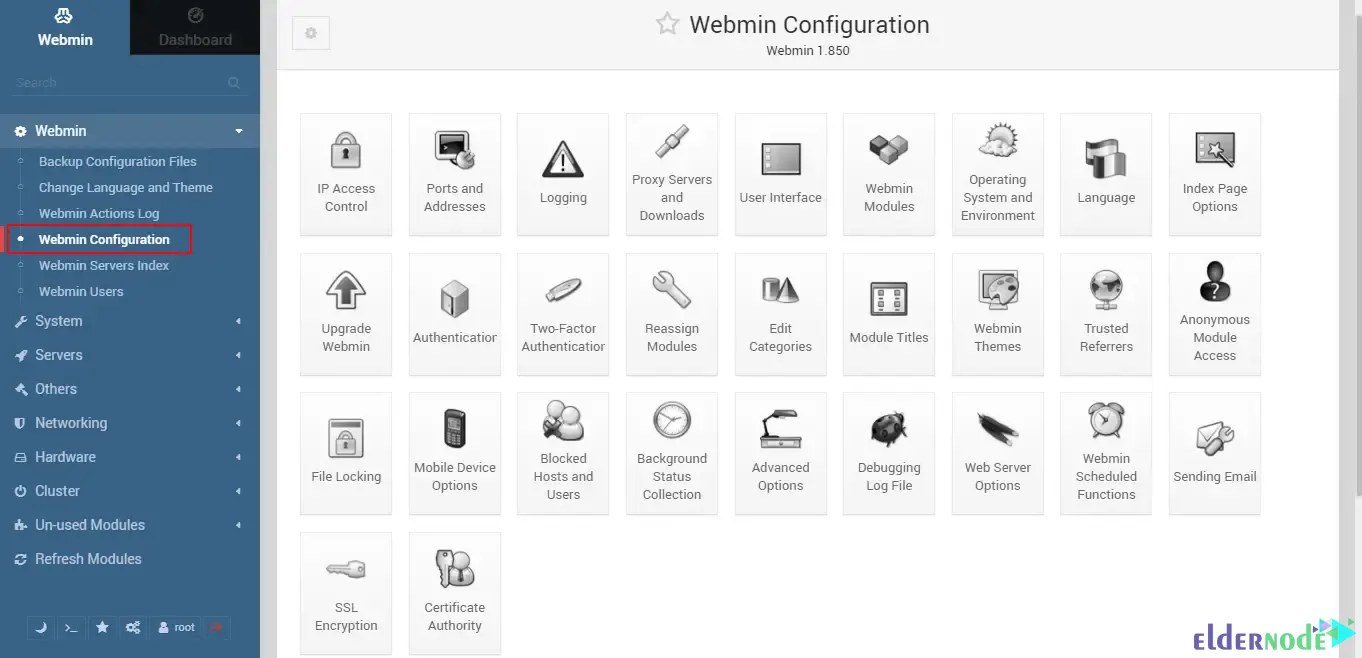
Attackers Prevention
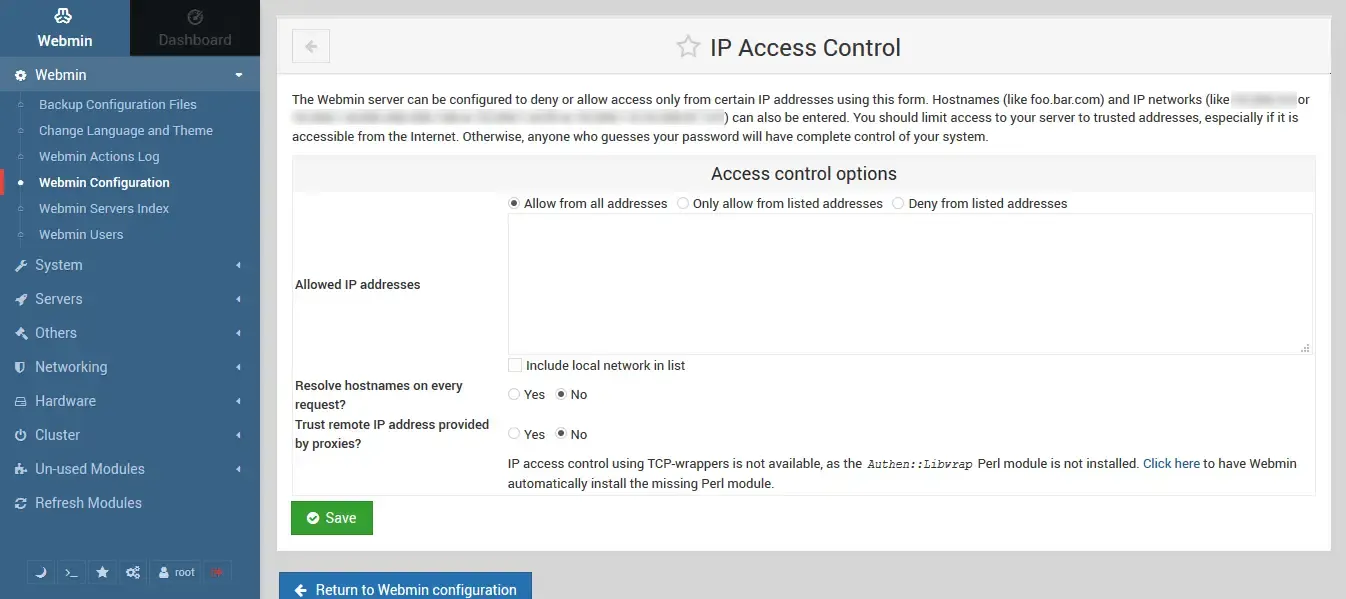
Webmin has built-in tools to keep attackers out. The IP Access Manager section allows you to allow or block specific IPs. Depending on whether you want to block or allow IPs, select “Only allow from listed addresses” or “Deny from listed addresses” and enter the IPs you want to block or allow in the “Allowed IP address” box:
Also, Webmin has options to block IPs with too many failed logins, which you can configure on the “Authenticator” page. By default, IP addresses with 5 failed logins will be blocked for one minute, but you can increase it. You can also block a user in the same way by enabling the “Block users with more than…” checkbox:

Webmin also has two-factor authentication that you can configure from the configuration page.
SSL Encryption
By default, Webmin uses an auto-generated, self-signed certificate. To configure Webmin to use a different certificate, go to the SSL Configuration section. Then you can upload your certificate from the “Upload Certificate” tab.
Go to Let’s Encrypt, an automated certification authority, to get an SSL certificate. To use Let’s Encrypt, you need a hostname and Apache or another web server installed:
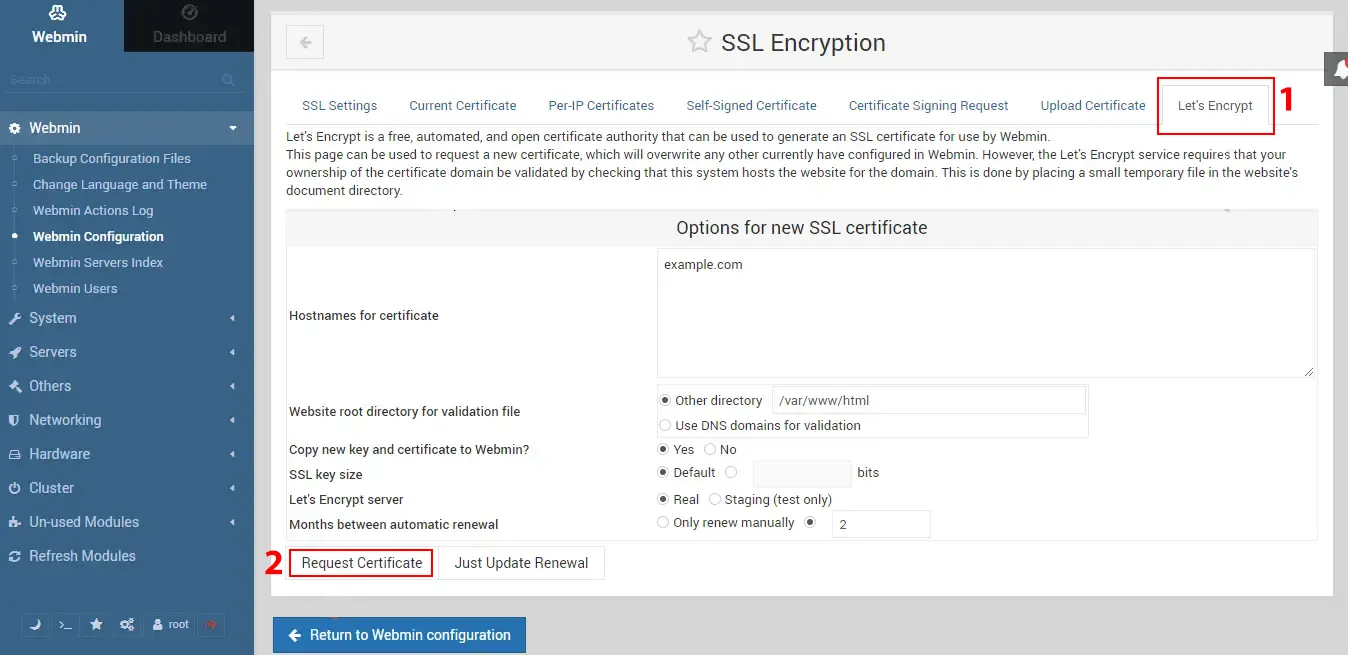
Configuring Server Settings with Webmin
You can configure server settings with Webmin through the web-based interface. To do so, after logging in, choose the specific server module related to the settings you want to configure. Within the selected module, you will find dedicated sections or menus for configuring different aspects of the server. These sections may include options like virtual hosts, network interfaces, or database access. By modifying the settings, you can customize the server configuration according to your requirements. Once you have made the desired changes, remember to save and apply them to the server. Also, remember to test the configuration to ensure the changes have been successfully implemented. Overall, you can repeat the process for other server settings by exploring the modules available in Webmin. Lastly, log out of Webmin when you have finished configuring the server settings.
Optimizing Server Performance with Webmin
Webmin is a web-based system administration tool that provides a GUI for managing servers. While it doesn’t directly optimize server performance, it offers a range of features that indirectly contribute to performance optimization. With Webmin, you can monitor system metrics, diagnose performance issues, and configure server services such as Apache, Nginx, MySQL, and PHP. By fine-tuning these services and analyzing system logs, you can identify and address performance bottlenecks. Webmin also allows you to manage firewall rules, schedule tasks, and keep your server software up to date, all of which can have a positive impact on performance. Although Webmin is a helpful tool, optimizing server performance requires a comprehensive understanding of various factors and techniques beyond the capabilities of Webmin alone.
Troubleshooting Common Server Issues with Webmin
Webmin can encounter issues that may affect its functionality. Here are some common server issues with Webmin and troubleshooting steps to resolve them:

Webmin Not Accessible
To address this issue, ensure that the Webmin service is running on the server. Verify that the server’s firewall allows incoming connections on the Webmin port (default is 10000). Also, check if the server’s network configuration is correct, including IP address and DNS settings. Finally, restart the Webmin service and try accessing it again.
Login Issues
Make sure you are using the correct username and password to log in to Webmin. Check if the user account has the necessary permissions to access Webmin. Also, you can reset the Webmin password if necessary. Lastly if not solved clear your browser cache and cookies and try logging in again.
SSL Certificate Errors
If you are using HTTPS to access Webmin, ensure that the SSL certificate is valid and properly configured. Also, check if the certificate has expired or if there are any certificate chain issues. Lastly, update or renew the SSL certificate and restart the Webmin service.
Module Installation Problems
Firstly, verify that the required dependencies for the module are installed on the server. Check the Webmin module documentation for any specific installation instructions. Also, ensure that the module file is in the correct directory and has the correct permissions. Lastly, restart the Webmin service after installing a new module.
Resource Usage and Performance
Monitor the server’s resource usage, such as CPU, memory, and disk space. Also, check for any processes or services consuming excessive resources. Then, optimize server configuration settings, such as increasing memory limits or adjusting caching mechanisms. Lastly, consider upgrading the server hardware if resource limitations are consistently causing performance issues.
Conclusion
Webmin is a powerful web-based system administration tool that empowers server management with its user-friendly interface and comprehensive features. It simplifies server configuration, monitoring, user management, file management, security, package management, and more. With Webmin, businesses can improve efficiency, enhance security, centralize server management, and benefit from its accessibility and community support.