
TTL mean in DNS and networking. In this article, we are going to serve you with the topic of TTL in DNS and network.
TTL is slightly different in DNS and networking, but overall it is the same.
What does TTL mean in DNS and networking?
TTL stands for Time To Live. We first define TTL in the network and then define TTL in DNS.
TTL on the network
TTL in a network is the life span of a package when switching between two or more systems.
When a packet is sent to a network, a time node (TTL) is considered for that packet, and after that time, the packet will be completely destroyed.
For example, to see the TTL of a package, you can use the Ping command and find out the TTL value of your ICMP package.
Note the image below:
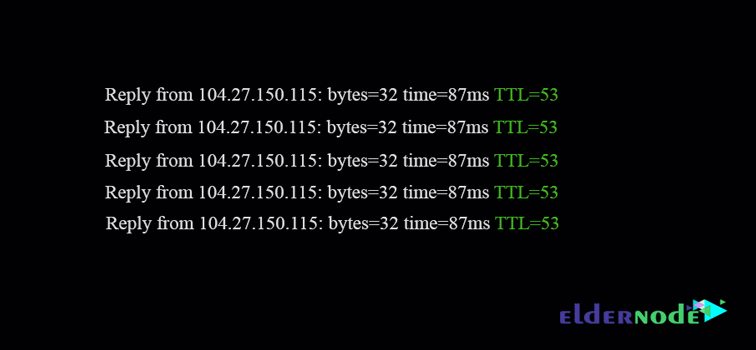
As you can see, TTL value for this package is 64 and this means that the package after the rejection of a 64-node disappears.
By default, Linux based systems send packets at 64 and Windows-based systems at 128.
Note: The TTL value will be reduced by default after each router is passed on the path, unless there are settings in the router that do not deduct TTL.
So far, you’re familiar with the concept of TTL on the network. Here’s the TTL concept in DNS.
TTL in DNS
TTL in DNS means life time, But not closed life sent; When you enter a domain name in your browser’s address bar, By DNS domain name to IP returns And this IP address and domain will be stored in your system cache so that you don’t need to request DNS next time and your speed will increase.
TTL in DNS is the amount of time that IP address and domain has been cached for you.
In network TTL, the value of TTL is only one. But TTL in DNS is set in seconds and works every second.
If you have any questions or problems, you can ask the Ask system to provide guidance.




