
[Updated] Written in Erlang language, Apache CouchDB is a free, reliable NoSQL database engine that natively supports data in JSON format. This makes it more scalable and easy to model your data as opposed to traditional SQL relational databases such as MySQL. The killer feature in CouchDB is its replication which spans a wide spectrum of computing devices and various computing environments to provide high availability and on-demand access to data. In this article, we try to introduce you to the Tutorial Install Apache CouchDB on CentOS 8. You can visit the packages available in Eldernode to purchase a CentOS VPS server.
Table of Contents
How to Install Apache CouchDB on CentOS 8
Let’s walk through the steps of this article to learn how to install Apache CouchDB on CentOS 8. Please join us.
Install the EPEL Repository
Firstly, you need to install the EPEL repository on CentOS 8.
yum install epel-release Enable the CouchDB Repository
In this step, you will proceed and enable the CouchDB repository by first creating a repository file, as you have successfully installed the EPEL package.
vi /etc/yum.repos.d/apache-couchdb.repo Paste the configuration below in the repository file and save.
[bintray--apache-couchdb-rpm] name=bintray--apache-couchdb-rpm baseurl=http://apache.bintray.com/couchdb-rpm/el$releasever/$basearch/ gpgcheck=0 repo_gpgcheck=0 enabled=1 Install CouchDB on CentOS 8
With the CouchDB repository defined in its configuration file, use the following command to proceed and install CouchDB.
yum install couchdb Once you installed the CouchDB package and its dependencies successfully, start, enable CouchDB to start on boot, and verify the status by running the commands.
systemctl start couchdb systemctl enable couchdb systemctl status couchdbTo verify the CouchDB listening port 5984:
netstat -pnltuHow to Configure CouchDB on CentOS 8
CouchDB can be configured either as a standalone mode or in a clustered mode. In this guide, however, you are going to configure the CouchDB server in the single-mode configuration. Also, you will configure CouchDB such that we can access it via a web browser.
CouchDB’s configuration files are located in the /opt/couchdb/etc/ directory. You are going to make a few configurations in the local.ini file. So open the file using your favorite editor.
vi /opt/couchdb/etc/local.ini In the [admins] section, create an admin account by uncommenting the line just below it and define the password for admin in the format.
[admins] admin = mypasswordNext, scroll to the [chttpd] section. Uncomment the port and bind-address values. Also, set the bind-address to 0.0.0.0 to allow access from external IP addresses. You can later change this value for security reasons.
[chttpd] port = 5984 bind_address = 0.0.0.0Save the changes and exit the configuration file. For the changes to take effect, restart CouchDB.
systemctl restart couchdb If you are running a firewall on the server, you must open port 5984 to allow traffic to CouchDB.
firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-port=5984/tcp firewall-cmd --reloadHow to Access CouchDB Web Interface
Going by our configuration, CouchDB should be running at localhost:5984. To confirm that CouchDB is working as expected, use the curl command to print CouchDB’s information in JSON format.
curl http://127.0.0.1:5984/ You can further confirm that all went according to a plan by firing up your browser and browsing your server’s IP address as shown.
http://server-ip:5984/_utils/You should get the webpage below prompting you to log in using the username and password as you defined in the local.ini file and hit ENTER.
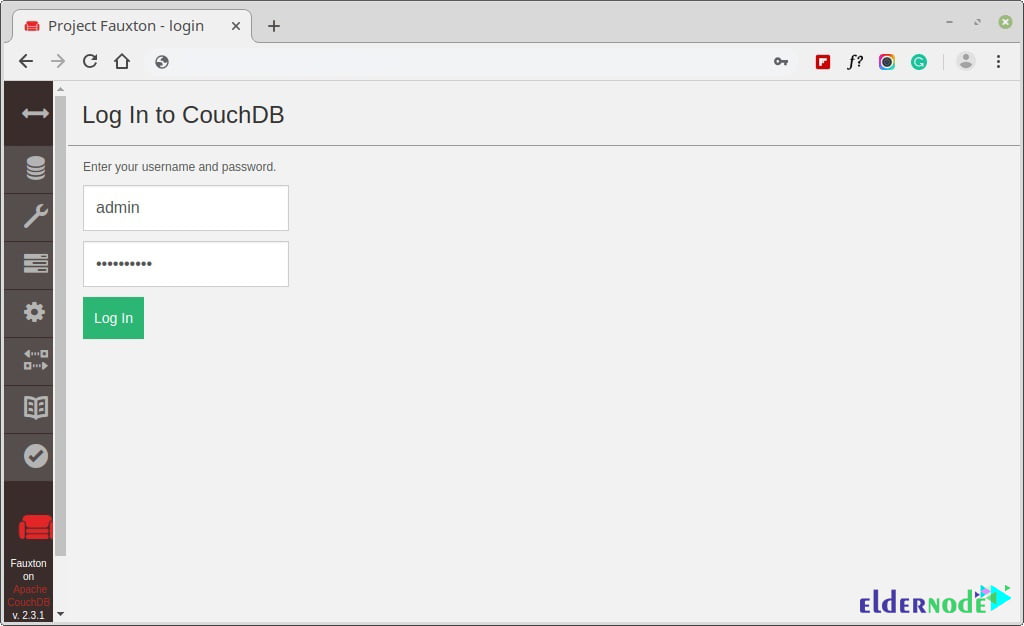
The dashboard will be displayed as shown below.

Nothing is displayed because you have not created any databases thus far. In the next section, you will create a few databases.
How to Create Databases in CouchDB
To create a database in CouchDB on the terminal, use the curl command in the syntax shown.
curl -u ADMINUSER:PASSWORD -X PUT http://127.0.0.1:5984 You are going to create 3 databases: eldernode_db, users_db, and production_db.
curl -u admin:P@ssword123 -X PUT http://127.0.0.1:5984/production_db curl -u admin:P@ssword123 -X PUT http://127.0.0.1:5984/eldernode_db curl -u admin:P@ssword123 -X PUT http://127.0.0.1:5984/users_dbFor each command, you should get the output below.
{“Ok”: true}To check the databases created using the GET parameter in the command.
curl -u admin:P@ssword123 -X GET http://127.0.0.1:5984/production_db curl -u admin:P@ssword123 -X GET http://127.0.0.1:5984/eldernode_db curl -u admin:P@ssword123 -X GET http://127.0.0.1:5984/users_db curl -u admin:P@ssword123 -X GET http://127.0.0.1:5984/_all_dbsAnd to view the databases on your browser, simply refresh/reload your browser.
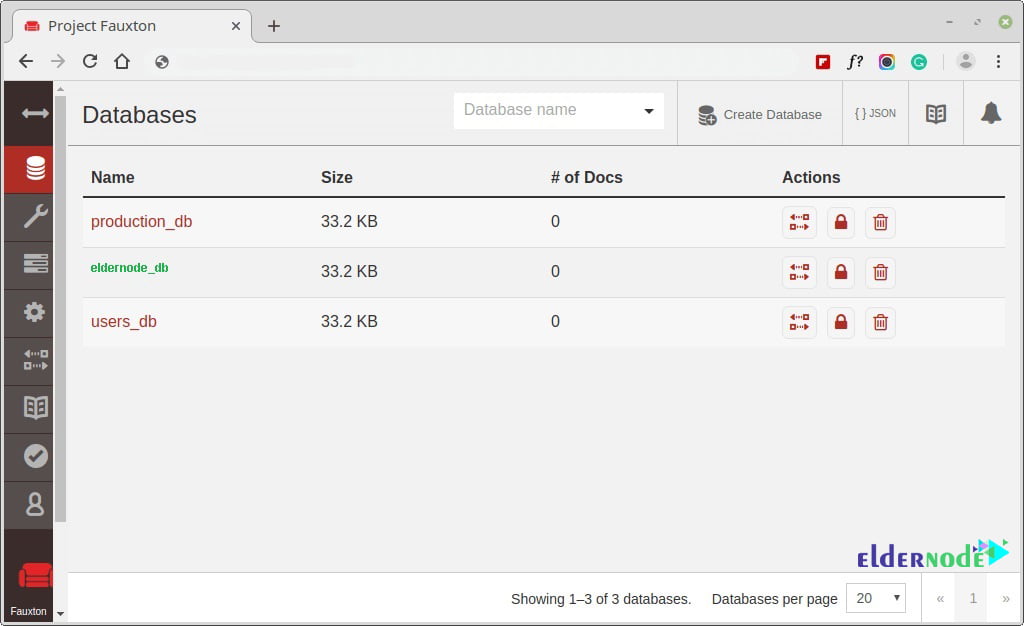
Also, to delete a database, use the delete parameter as shown. For example, the command deletes users_db database.
curl -u admin:P@ssword123 -X DELETE http://127.0.0.1:5984/users_db Run the command below to check the databases again.
curl -u admin:P@ssword123 -X GET http://127.0.0.1:5984/_all_dbs As you can observe, only two databases are present as we have deleted the users_db database.
Conclusion
In this article, you succeeded to finish learning Tutorial Install Apache CouchDB on CentOS 8. From now on you will be able to install and configure CouchDB on CentOS 8 system comfortably.





How to configure SELinux and Firewall?
since the SELinux is enabled in your system, you are recommended to disable it in your system. To disable the SELinux by editing /etc/selinux/config file:
nano /etc/selinux/configIs it possible to verify CouchDB installation?
Since the CouchDB server is running at localhost:5984, you can verify whether your installation is successful or not. To print information about CouchDB database, run the following command:
curl http://127.0.0.1:5984/what for installing apache webserver?
Use the command below to install Apache service
sudo yum install httpdIs MongoDB better than CouchDB?
They both scale across multiple nodes easily, but MongoDB favours consistency while CouchDB favours availability
which is fastest? NoSQL or SQL?
Any of them is not faster than another one in general. I mean NoSQL databases are specifically designed for unstructured data which can be document-oriented, column-oriented, graph-based, etc. In this case, a particular data entity is stored together and not partitioned.