
A Linux system administrator needs to know some Linux tricks. In this article, you are going to learn how to disable SELinux temporarily or permanently. Linux, as the most secure operating system you can use for its illustrious security implementation features. Join us to check the status of SELinux and also disable SELinux in CentOS/RHEL and Fedora, in case it is enabled.
Table of Contents
How to disable SELinux temporarily or permanently
SELinux is described as MAC (mandatory access control) security structure executed in the kernel for starters. SELinux offers some security policies which would otherwise not be effectively implemented by a System Administrator.
While installing the RHEL/CentOS, or its derivatives, the SELinux feature or service will be enabled by default, so some applications on your system may not actually support this security mechanism. Therefore, you have to disable or turn off SELinux to make such applications function normally.
Please note: pay attention to this tutorial to implement some mandatory access control on files and services to function properly, If you don’t want to disable SELinux.
How to disable SELinux in Linux
First, check the status of SELinux on your system, by running the following command:
sestatus 
Depending on what you want to achieve, you can do this temporarily or permanently after proceed to disable SELinux on your system.
Disable SELinux temporarily
Run the below command to disable SELinux temporarily.
echo 0 > /selinux/enforceAlso, you can use the setenforce tool alternatively.
setenforce 0Or, instead of 0, you can use the Permissive option.
setenforce PermissiveNote: the methods you read till here, would work until the next reboot, therefore to disable SELinux permanently, move to the next section.
Disable SELinux permanently
You need to open the file /etc/sysconfig/selinux , to disable SELinux permanently.
vi /etc/sysconfig/selinux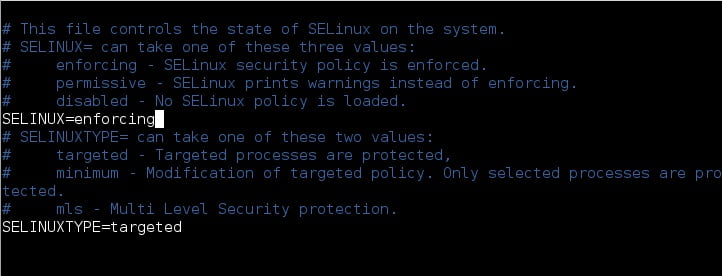
Now, you should change the directive SELinux=enforcing to SELinux=disabled.
SELINUX=disabled 
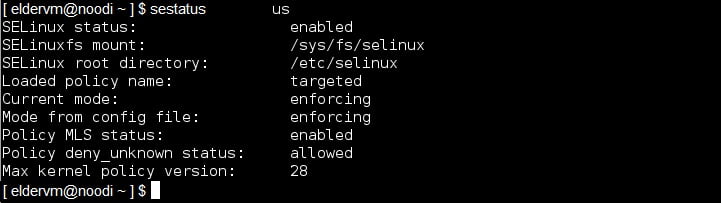
Next, save and exit the file to let the changes take effect. To do this, reboot your system or check the status of SELinux using sestatus command.
sestatus 
In conclusion,
You learned how to disable SELinux on CentOS/RHEL and Fedora.
Dear user, we hope you would enjoy this tutorial, you can ask questions about this training in the comments section, or to solve other problems in the field of Eldernode training, refer to the Ask page section and raise your problems in it.




![Install Wine 5.20 on Ubuntu 20.10 [New Release]](https://blog.eldernode.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/Install-Wine-5.20-on-Ubuntu-20.10-New-Release-300x164.png)

